What is Warehouse Logistics?
Warehouse logistics is all about the management of goods storage and movement within the facility. It defines everything that happens to an inventory after the manufacturer supplies it to a site: receiving, storing, picking, and shipping. They play an essential role in supply chain integration. Organizing warehouse operations consciously makes sure their customer saves on cost and gets the products timely to their subsequent points.
How are Warehouse Management and Logistics interconnected?
Logistics and Warehouse Management are intricately linked, with warehouse operations laying the foundation for the success of logistics. While logistics plans and moves goods along the supply chain, warehouse management is considered the discipline that manages physical storage and internal flow. Their integration promotes supply chain coordination for order accuracy, lower cost, and faster delivery.

Inventory Management
Infrastructure and equipment for warehouse operations ensure inventory is properly organized and stored leading to correct inventory records. On the other hand, logistics ensures timely movement of inventory. Thus, they complement each other to inventory control, avoid overstocking or stock-outs, and provide for warehouses and logistics operations.
Order Fulfilment
Warehouse logistics fulfils orders through the complementary interaction of warehousing activities with logistics, moving goods strategically through the logistics system with the right picking, packing, and dispatching from the warehouse. The synergy between the systems leads to fewer errors, better delivery schedules, and customer satisfaction.
Space and Layout Planning
An Efficient Warehouse Layout streamlines the flow of goods thereby reducing travel time and labour costs. The space is maximally used through intelligent design to increase productivity, facilitate cross-docking, and accelerate materials handling. Good layout planning is necessary for high-performing and cost-effective warehouse and logistics operations.
Information Flow
With the Warehouse Management System (WMS) integration, inventory is tracked in real time while an information flow occurs between logistics and warehouse teams. This information assists in shipment scheduling, route planning, and demand forecasting and thus elevates the decision-making and performance efficiency of the whole supply chain.
Continuous Improvement
Warehouse logistics is all about continuous improvement, working to enhance order accuracy, picking speed, storage practices, etc. By studying trends through data and working in close collaboration, both logistics and warehouse functions eliminate inefficiencies and continue to adjust to demand changes, raising the performance level of the whole supply chain.
Types of Warehousing in Logistics
Several warehouse types, which are public warehousing, private warehousing, contract warehousing, distribution centres, cross-docking, cold storage warehousing, and automated storage systems, exist to meet different storage and logistics requirements.
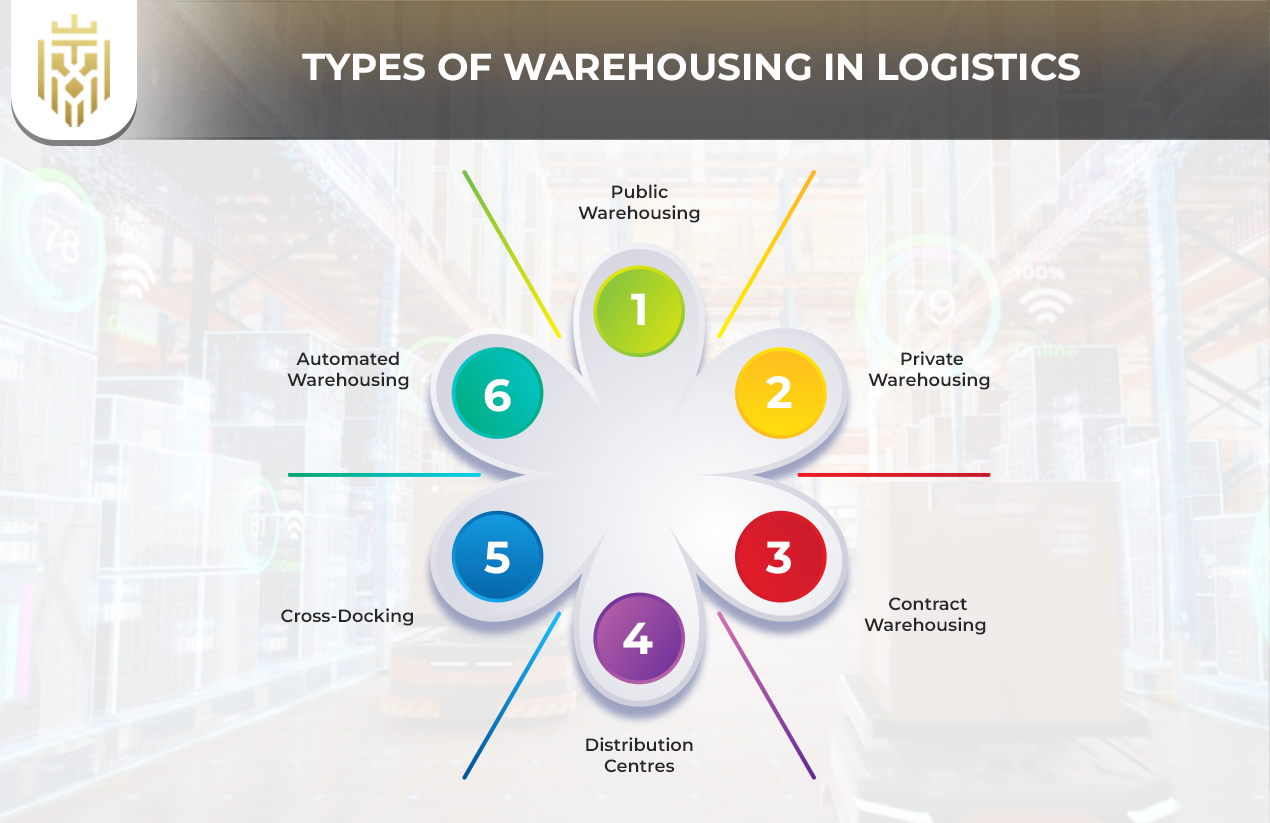
Public Warehousing
Public warehousing is a form of warehouse in logistics wherein businesses lease storage space from third-party providers. This is a flexible and cost-effective option that suits small and seasonal businesses that do not want to make the long-term investment of owning a facility but require basic services like inventory tracking, packing, and shipping.
Private Warehousing
Private warehouses are entirely controlled operationally by the particular company that owns them. This kind of warehouse in logistics is suitable for businesses with high requirements for secure, tailor-made solutions for huge quantities of inventories that aid the companies in the internal logistics of the company for tracking and standardising processes.
Contract Warehousing
Contract warehousing marries public warehousing flexibility with the controls private facilities have. Hence, long-term storage, specialized services, and dedicated space under third-party management form a strategic option for companies aiming to outsource some of their operations to reliable logistics partners.
Distribution Centres
Distribution logistics ensures fast, localised delivery by breaking bulk shipments into smaller, manageable loads. An example would be cold storage warehousing, which maintains perishable product quality along with improvements in regional supply chain performance. An efficient distribution system reduces delivery times and increases order precision while delivering superior customer satisfaction.
Cross-Docking
Cross-docking is a method that plus warehouse logistics sales minimization of storing time. As such, goods are sorted then quickly reloaded to avoid double handling costs and storage costs. This type of arrangement is best suited where an operation is time-sensitive or fast-moving, and thus it is the very backbone of any modern logistics network.
Automated Warehousing
The combination of robotics and conveyor belts along with AI software within Automated Storage Systems enables faster warehousing operations by eliminating repetitive tasks. They ensure higher accuracy and accelerate processing while reducing human error which positions them as vital components in modern logistics and warehouse management models.
Warehouse Logistics Components
Warehouses operate through warehouse management and warehouse operations while the third component, warehouse management systems (WMS) with inventory control direct order fulfilment and efficient warehouse layout alongside material handling and cold storage and technology integration boosts workplace efficiency.
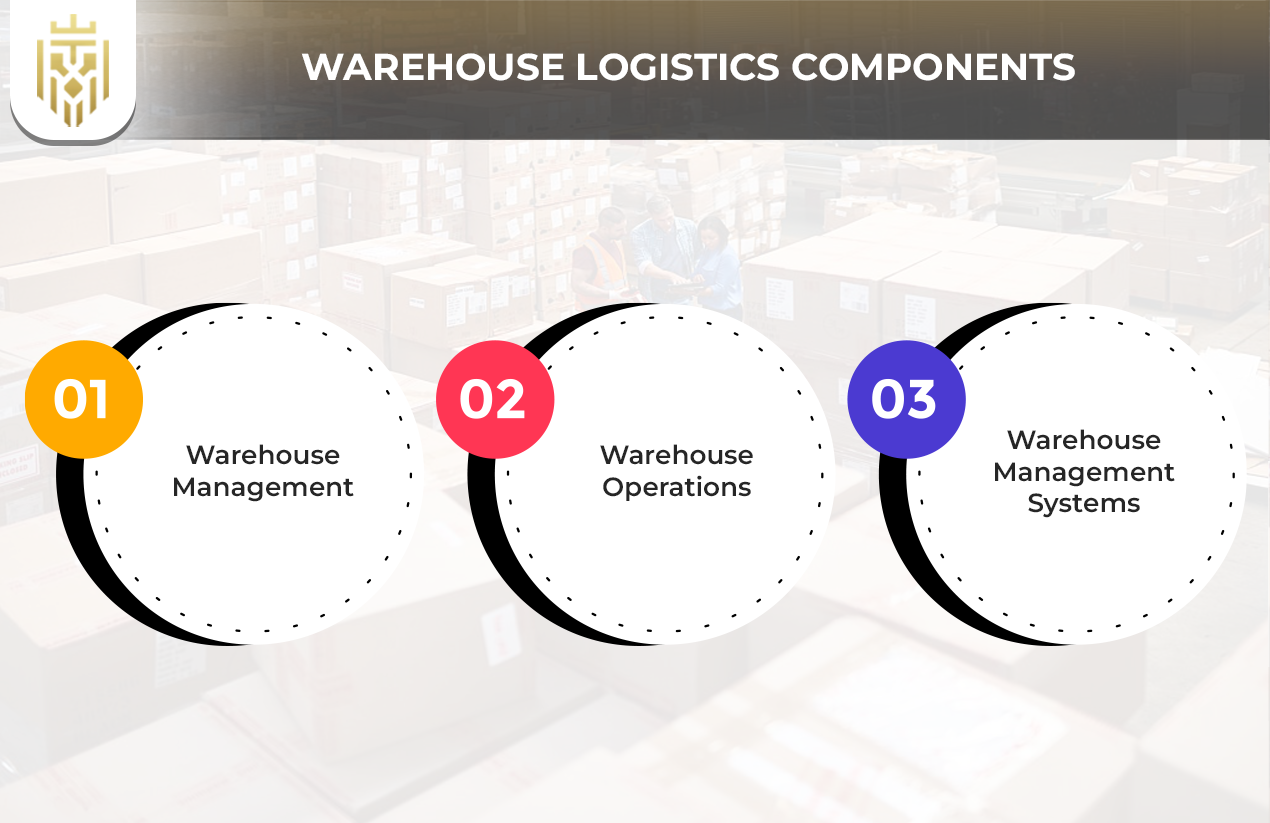
Warehouse Management
Warehouse management controls all warehouse functions including storage organization and processing orders. Through effective warehouse management it brings together best practices and runs operations better to create smooth product flows and correct data while speeding up the entire distribution process.
Warehouse Operations
Forklifts and pallet jacks enable warehouse handling equipment to handle goods effectively throughout warehouse operations. These equipment types make inventory movement happen faster at receiving, order packing, and order shipping areas. Better warehouse processes help us achieve fast orders and minimize manual work.
Warehouse Management Systems
Through warehouse management systems, organizations achieve complete digital control over inventory movements and order tracking and storage locations. Real-time data accessibility enables companies to accurately maintain stock levels while increasing staff productivity and improving operational coordination between warehouse activities and logistics operations.
Challenges of Warehouse Logistics
The operation of logistics activities faces major difficulties because of space constraints, inventory accuracy, labour management, seasonal demand variations, technology integration, and maintaining supply chain coordination that prevent from promoting cost-effective and smooth operations.
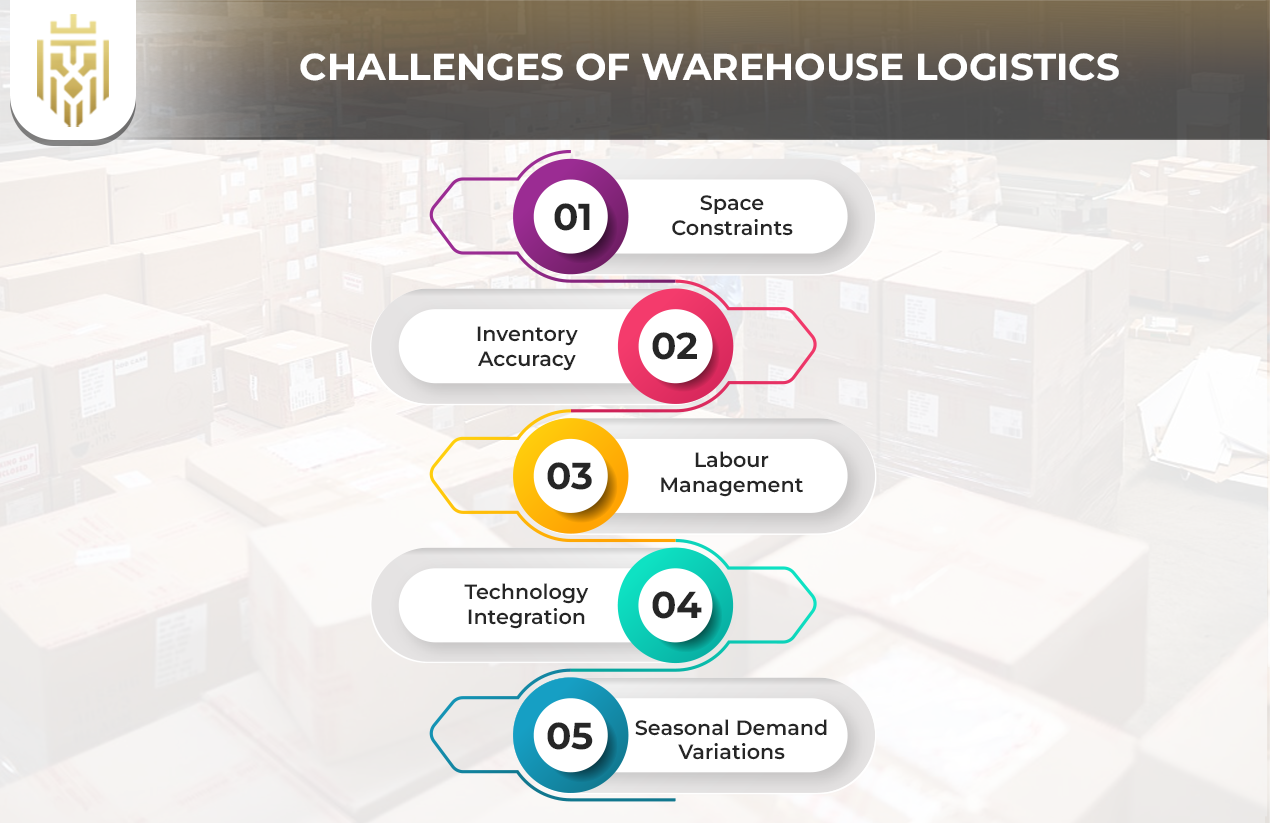
Space constraints
The limited space available in warehouses creates difficulties in logistics operations that lead to unsatisfactory warehouse layouts and slow order management processes. The implementation of vertical storage solutions with better racking systems and automated storage solutions enables warehouse optimization for improved product accessibility.
Inventory Accuracy
Wrong inventory counts result in delayed order delivery while creating inventory surplus or deficits. Organizational training coupled with specific task assignment additionally motivational incentives enhance workforce output thus maintaining stable warehouse performance.
Labour Management
Warehouse logistics faces labour challenges because of excessive employee replacement needs and insufficient workforce levels and insufficient employee skillsets. Training programs combined with clear task allocation and incentive structures drive labour productivity improvements that lead to sustained warehouse service delivery levels.
Technology Integration
The implementation of new logistics and warehouse management technologies faces challenges because they differ significantly in price and demand knowledge and operational compatibility. Businesses must surpass these implementation obstacles to maintain their competitiveness and rise in operational efficiency while protecting their warehouses against future growth requirements.
Seasonal Demand Variations
Seasonal variations in customer demand create problems with storage areas and worker requirements. Businesses employ warehouse logistics frameworks with forecasting methods and adaptable space plans to handle inventory effectively while meeting customer demands throughout peak selling seasons.
Benefits Of Warehouse Logistics
Warehouse logistics improves inventory accuracy, enhances order fulfilment, ensures cost efficiency, supports scalability, boosts customer satisfaction, provides real-time visibility, and strengthens supply chain resilience, making operations more reliable and competitive.
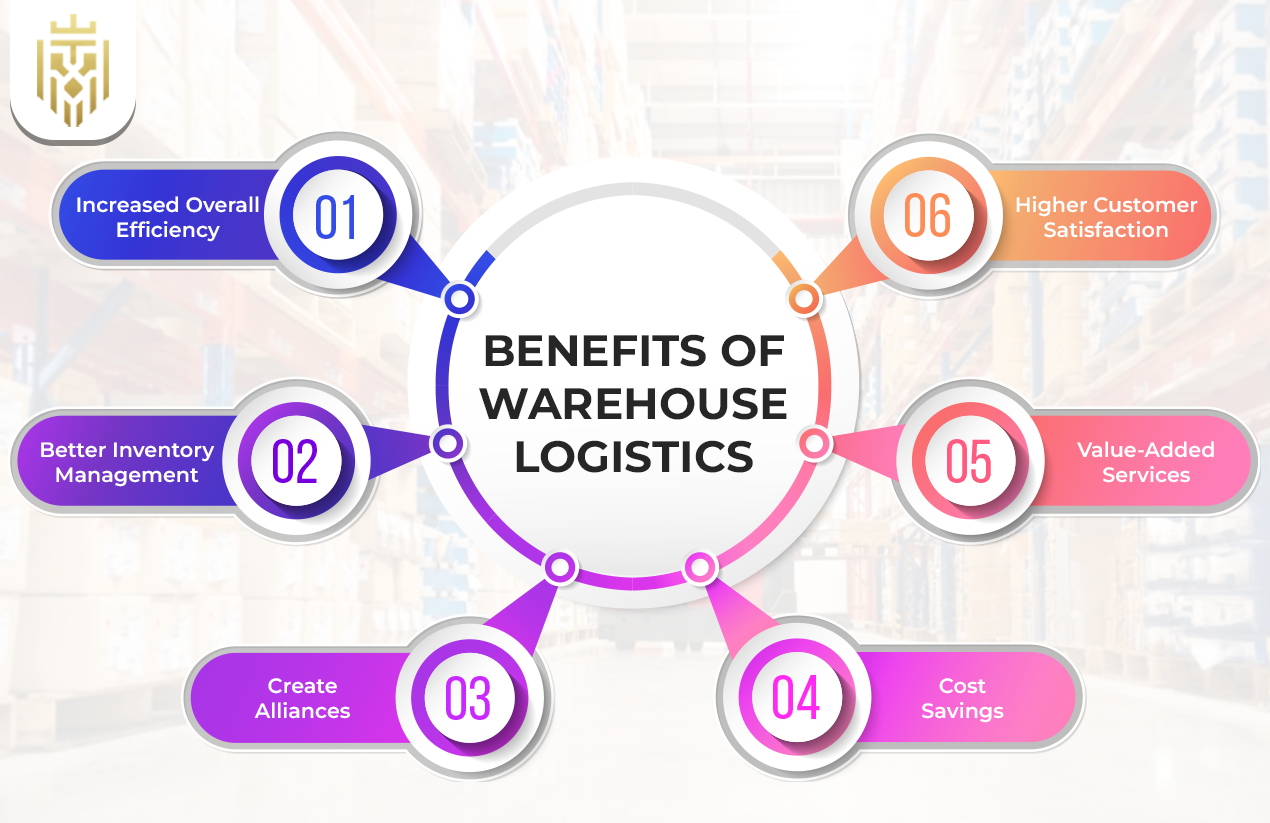
Increased Overall Efficiency
Businesses achieve faster order picking and inventory restocking operations through the implementation of Warehouse Management Systems and automated storage systems. These processes drive down mistakes while speeding up deliveries and boosting operational efficiency which supply chains need today.
Better Inventory Management
Warehouse logistics heightens inventory precision while also decreasing stock loss. Through strategic alliances within warehouse logistics operations organizations can expand their service offerings while lowering operational expenses.
Create Alliances
Through strategic warehouse logistics collaboration companies gain extends their service offerings and achieve reduced operational expenses. Companies that apply effective warehouse logistics practices reduce their costs related to labour expenses as well as space usage and transportation expenditures.
Cost Savings
Companies that adopt efficient warehouse logistics methods can achieve substantial reductions in labour costs along with spatial usage and transportation expenditures. The modern warehouse sector extends its offerings from basic storage to include bundling, labelling, and reverse logistics services.
Value-Added Services
The advanced warehouse logistics infrastructure delivers storage-related services together with bundling solutions and labelling functions as well as reverse logistics capabilities. Operating efficiency remains untouched when companies deploy these value-added services which offer superior service quality and tailored solutions for specific clients.
Higher Customer Satisfaction
Warehouse logistics enables companies to meet customer requirements through accurate tracking and optimised picking combined with timely delivery processes. The speed and accuracy of deliveries generate trust between businesses and customers which leads to repeat orders and warehouse operations emerge as major factors for brand loyalty and satisfaction.
How to Overcome Warehouse Logistics Challenges?
Businesses must establish an efficient warehouse layout and deploy a dependable Warehouse Management System along with improved teamwork coordination to tackle warehouse logistics issues. The improved logistics network achieves seamless operations with decreased errors and enhanced performance which guarantees enduring success for businesses operating in dynamic markets.
FAQs
1) What is Warehouse Logistics?
Warehouse logistics is all about the management of goods storage and movement within the facility. It defines everything that happens to an inventory after the manufacturer supplies it to a site: receiving, storing, picking, and shipping.
2) What are the functions of Warehouse Logistics?
The warehouse logistics operations cover inventory management, receiving and storing goods, order picking, packing, shipping, tracking, cold storage warehousing, using warehouse handling equipment, and ensuring supply chain coordination and data accuracy.
3) What are the types of Warehouse Logistics?
Several warehouse types, which are public warehousing, private warehousing, contract warehousing, distribution centres, cross-docking, cold storage warehousing, and automated storage systems, exist to meet different storage and logistics requirements.
4) What are the components of Warehouse Logistics?
Warehouses operate through warehouse management and warehouse operations while the third component, warehouse management systems (WMS) with inventory control direct order fulfilment and efficient warehouse layout alongside material handling and cold storage and technology integration boosts workplace efficiency.
5) What are the challenges of Warehouse Logistics?
The operation of logistics activities faces major difficulties because of space constraints, inventory accuracy, labour management, seasonal demand variations, technology integration, and maintaining supply chain coordination that prevent from promoting cost-effective and smooth operations.