Block Chain Technology
It is a decentralized digital ledger wherein records are protected and guaranteed against tampering. Each transaction is stored in a “block,” and it is linked to all previously generated blocks, thus making any alteration detectable. This technology removes the requirement for an intermediary unlike other systems, thereby making data-sharing faster and much more reliable.
Today, this technology is no longer confined to cryptocurrency but has spread across various sectors like healthcare, finance, and even logistics. With supply systems, it is expected to resolve some unresolved problems related to viewing, trusting, and efficiency.
Understanding Blockchain in Supply Chain
In modern supply chains, many stakeholders spread across countries-from raw material suppliers to manufacturers, distributors, and retailers-are in play. This complexity often results in delays, instances of information silos, and issues of trust. Blockchain deals with such issues by providing a shared system where all parties see the same verified information.
The presence of blockchain in the supply chain gives companies the possibility to streamline their processes, reduce paperwork, and facilitate smoother working together. Be it tracing the origin of material or checking for the legitimacy of delivery schedules, the blockchain is the one-point truth for all logistics operations worldwide.
Benefits of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
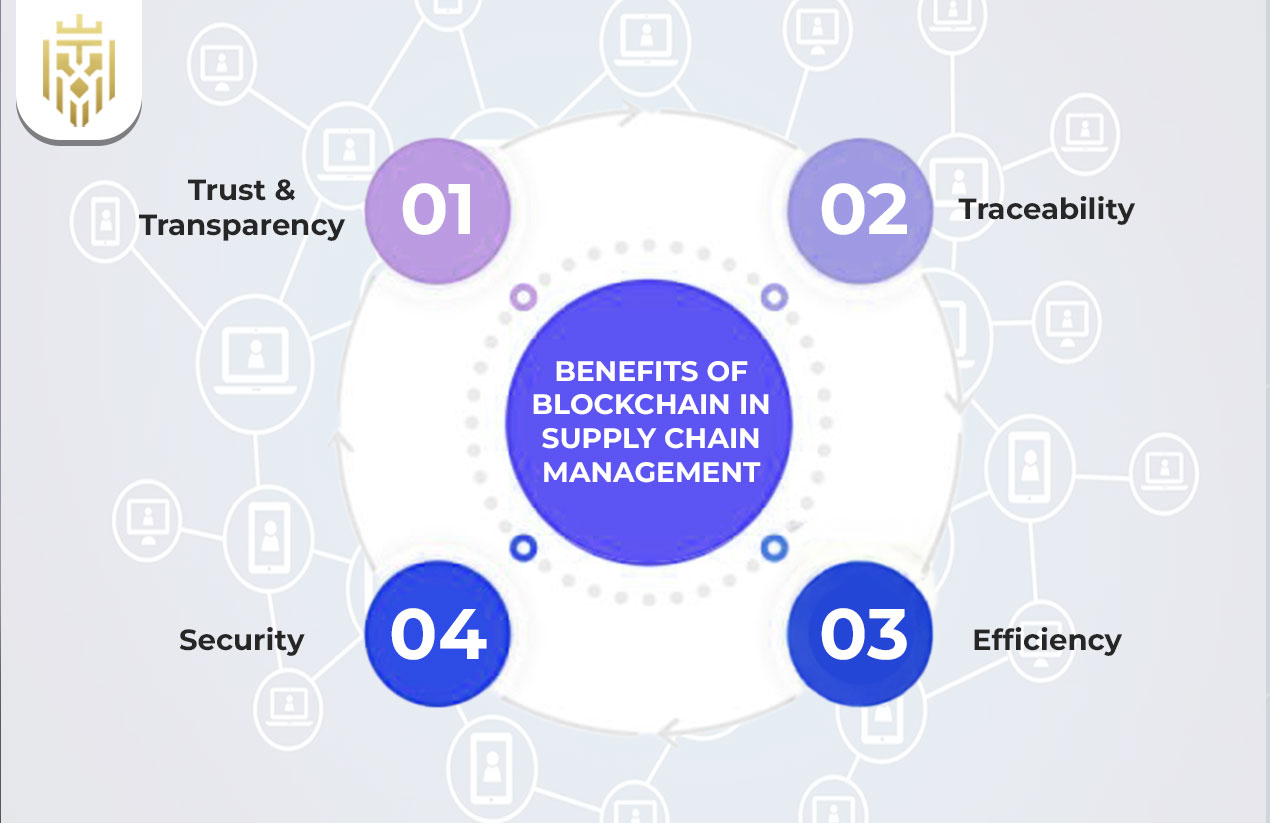
The advantages of blockchain go beyond cost savings—it helps reshape how supply chains are managed and monitored.
Trust & Transparency
Blockchain transactions are never hidden from participants due to the existence of immutable digital ledgers. For instance, retailers can check whether suppliers actually shipped goods on time while customers see the origins of a product. Such transparency ensures greater levels of trust in the supply chain relationship.
Traceability
Recall or fraud investigations are simpler where blockchain traces every movement of goods. For example, a food manufacturer can trace a produce back to the farm from where it was brought in less than a few minutes, thereby avoiding a bigger recall and severe damage to brand reputation.
Efficiency
Using smart contracts, blockchain can perform approvals, payments, and compliance checks automatically. If, for instance, a system automatically recognises that delivery has occurred, then it can trigger the release of payment. This minimises bottlenecks, allowing for faster turnaround times.
Security
Unlike traditional databases, blockchain cannot be manipulated by unauthorised users. Sensitive documents such as bills of lading, customs declarations, and quality certificates are secured on the blockchain, reducing the risk of fraud and cyberattacks.
Blockchain in Logistics
Logistics, being the backbone of global trade, benefits significantly from blockchain integration.
Tracking
Blockchain can track shipping at all points from warehouse dispatch to final delivery. From the logistics manager’s point of view, locations are under view, thus reducing uncertainty in delivery schedules and making modality-payment promises to customers.
Product Authenticity
Counterfeiting is a multi-billion-dollar issue in pharmaceuticals, fashion, and electronics. Blockchain thus creates a digital certificate of authenticity that assures that consumers and businesses are receiving only genuine production.
Inventory Management
Discrepancies in inventory are common among warehouses. Through blockchain, stock levels are updated in real time among all stakeholders, preventing costly errors such as stock being out or being in excess.
Risk Management
Delays, supplier failures, and geopolitical issues pose risks to global supply chains. Blockchain acts as an early warning system by recording evidence-backed information concerning supplier performance and logistics disruption, thus allowing for greater mitigation of those risks.
Fraud Prevention
Fraudulent invoices, duplication of shipments, and misrepresentation are some major challenges. Blockchain prevents such duplication or alteration by making sure that once a transaction has been recorded, it cannot be duplicated or amended.
Applications of Blockchain in Supply Chain
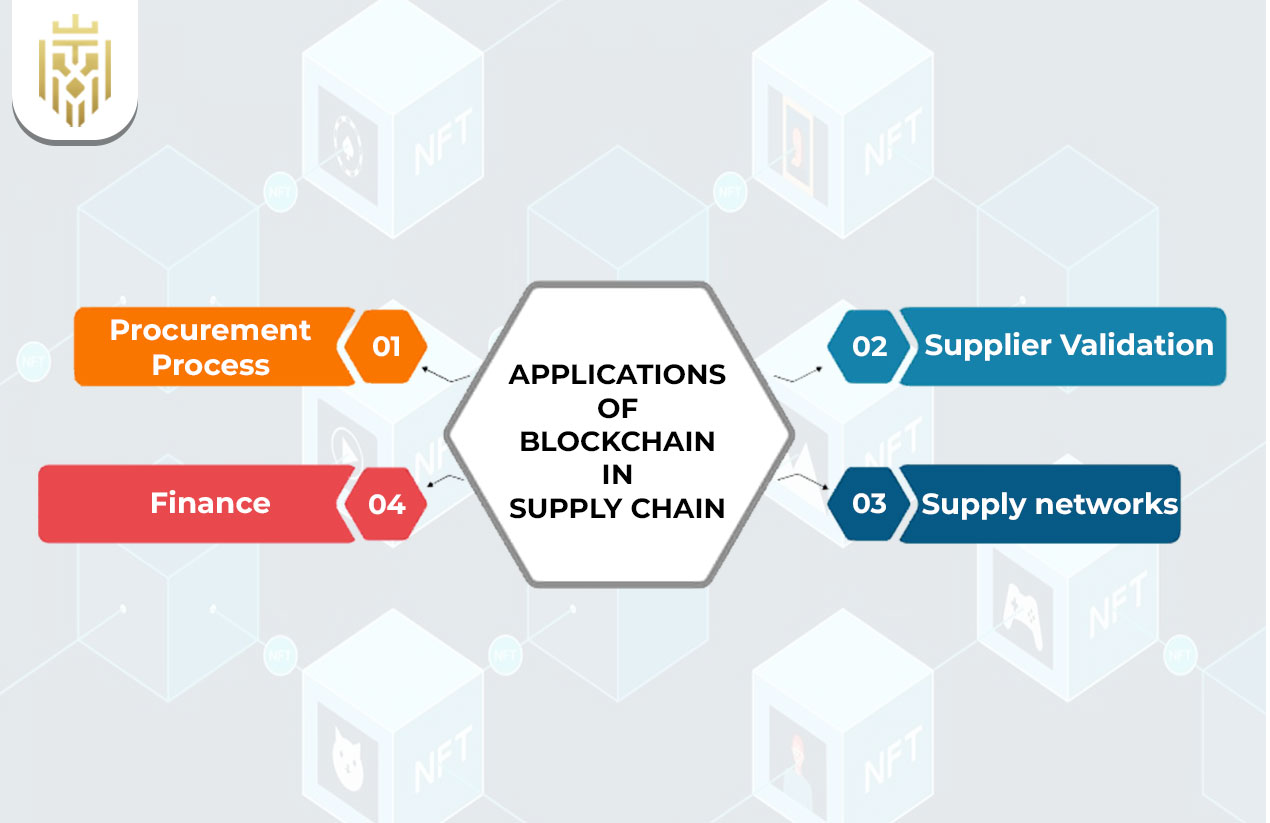
Blockchain is moving from concept to practice, with real-world applications transforming how supply chains operate. From procurement to payments, it enhances visibility, reduces errors, and builds trust across every stage of the logistics network.
Procurement Process
Among the challenges companies face during procurement are overbidding and lack of transparency. Blockchain assures fairness by recording every bid and contract permanently, thus diminishing the risk of corruption.
Supplier Validation
Onboarding suppliers is a time-consuming process. Blockchain stores certificates, compliance documents, past-history records in a secure digital form. This cuts down on delays and makes suppliers accountable.
Supply networks
Modern supply chains have dozens of partners working simultaneously through the network. Blockchain makes it easy to exchange data across the network with real-time updates to all parties, from transporters to retailers, thereby averting miscommunication and dis-coordination.
Finance
Accounting and financial accounting in supply chains are usually held up by delayed invoice approvals and payment processing. With blockchain, payments are automatically released by smart contracts upon fulfillment of predefined criteria such as confirmation of delivery, thereby diminishing financial cycle times while building trust.
Challenges of Supply Chain
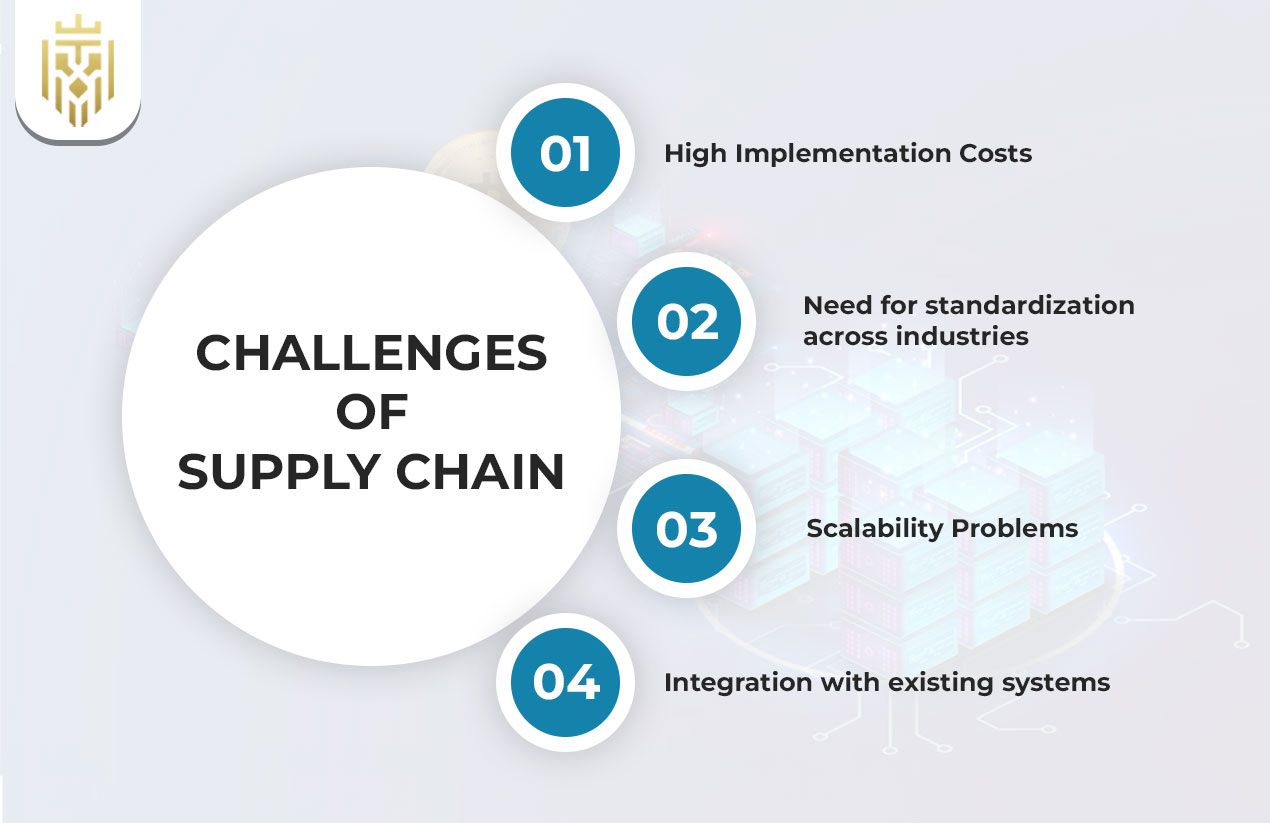
Despite its promising impact, adopting blockchain in supply chain management is not without challenges. Businesses must overcome issues related to cost, standardization, and scalability before blockchain can achieve widespread use.
High Implementation Costs
Setting up blockchain requires infrastructure investment, training, and system upgrades. This makes the cost of adopting it most businesses simply unaffordable. While large corporations are able to absorb such costs, small and mid-sized firms often cannot afford them.
Need for standardization across industries
If standards are not put together, various blockchain systems may fail to merge smoothly across supply chains, thus limiting collaborations between different players. Some kind of industry-wide consensus or even regulatory framework would be required to render blockchain universally compatible.
Scalability Problems
The operations of a supply chain increase in number, and blockchain networks may then face slower transaction speeds and higher energy use, making hurdles for large-scale operations. So it becomes difficult to retain the same efficiency throughout the global supply chains with high volumes of transactions.
Integration with existing systems
Most organizations are already dependent on ERP and WMS tools while integrating these with blockchain demands heavy planning and technical adjustments. Often containing its own core of specialized knowledge, the integration process can delay the adoption times quite a bit.
FAQs
1. How blockchain can improve supply chain?
The blockchain improves supply chains by offering real-time visibility, reducing disputes, and automating operations. From here, companies enjoy efficient operations, cost savings, and enhanced customer experience.
2. How does block chain handle data & security?
Blockchain encrypts, timestamps, and validates data in a decentralised manner. This makes it very difficult for hackers to penetrate and alter the data in any way that is illegal.
3. How does blockchain support compliance with international trade regulations?
Blockchain ensures traceability of every movement of the product to the customs, tax authorities, and regulators. Hence it greatly reduces the cost of compliance and facilitates cross-border trade.
4. How does blockchain improve sustainability in supply chains?
Blockchain follows the raw materials and processes and thereby assists companies in substantiating the claims of ethical and sustainable sourcing. It even reduces waste by advancing planning and transparency.