What Is Logistics Management?
Logistics management involves planning, implementing and controlling the smooth flow of goods and services between their origin and consumption. It ensures each movement aligns with the customer’s expectations and supports the business’s objectives as a part of the supply chain management.
Why Logistics Management Matters?
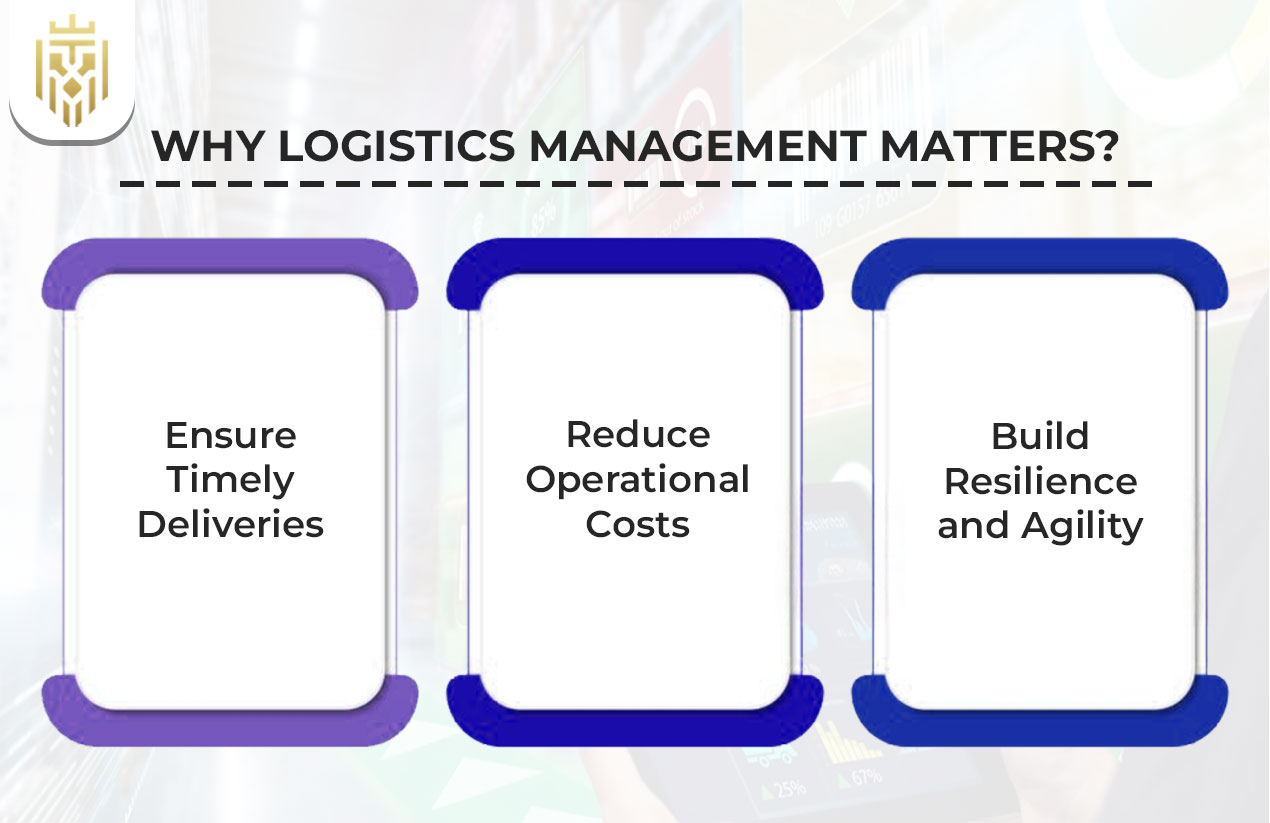
Learning ‘what is logistics management?’ is central to mastering modern chain management. It assists companies to match consumer demand through efficient supply system flow, improving operational control, profitability, and customer satisfaction throughout the distribution of the supply chain.
Ensure Timely Deliveries
Adequate logistics management enables the customers to receive goods at the right time and in an impeccable state. This trust increases satisfaction and creates loyalty that is a strong basis of long-term business success. Confidence in logistics operations enhances the level of services and customer retention.
Reduce Operational Costs
When the resources are optimised, the businesses effectively reduce unnecessary costs and enhance efficiency. Effective management logistics helps companies to uncover waste, reduce transport, and decrease warehousing costs. This saves a lot and eases the supply chain activities.
Build Resilience and Agility
Effective logistics helps companies adapt to sudden changes in volatile markets. Companies with excellent logistics systems can redirect shipments, replenish reserves and institute flexible supply flows, ensuring business continuity even with disruption in the supply distribution chain.
Core Components of Logistics Management
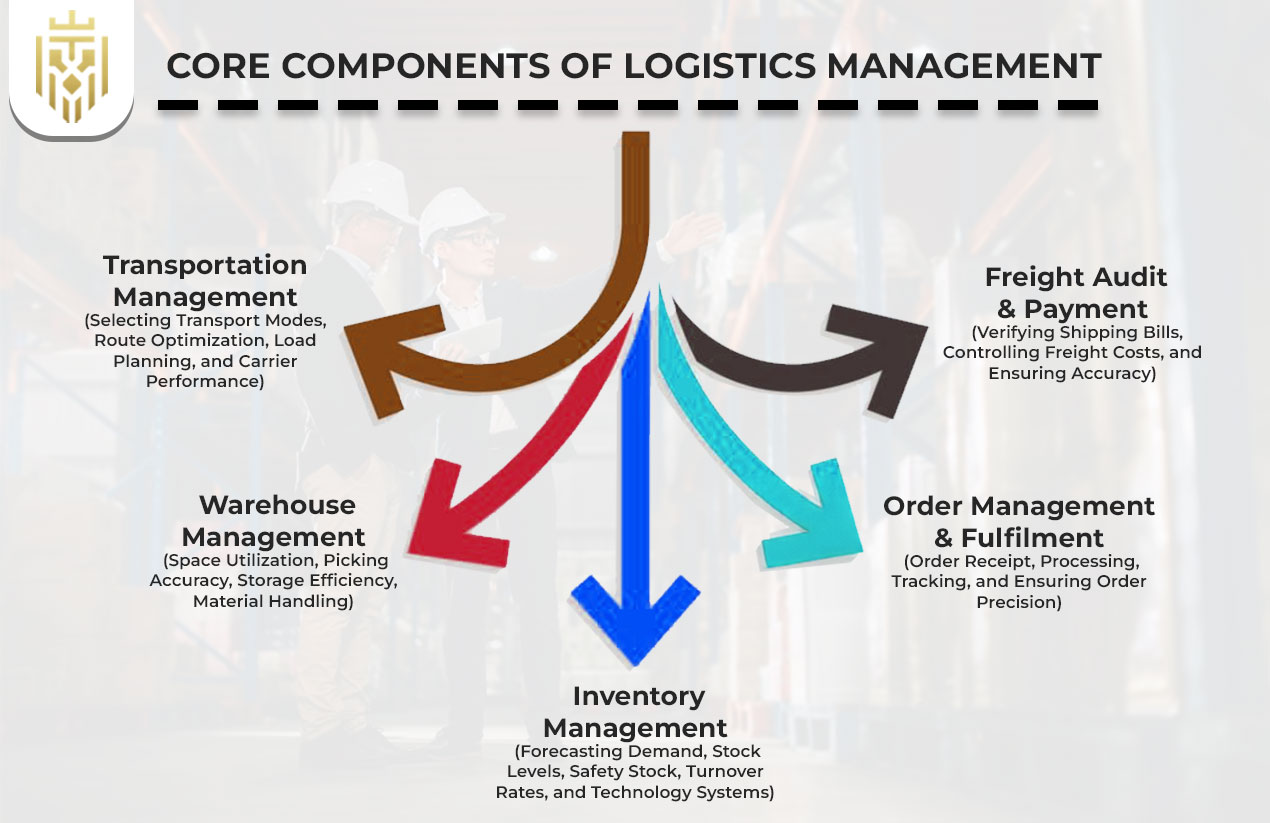
It is also important to know the main parts of learning logistics management. They are transportation, warehousing, inventory management and order fulfilment and they help in the effective execution of the supply chain and have a better business performance in both consistent and turbulent environments.
Transportation Management
In order to study logistics management, it is critical to learn about its main segments. These are transportation, warehousing, inventory control and order fulfilment, which all lead to the easier execution of a supply chain and better business performance both during times of stability as well as during a disruption.
Selecting Transport Modes, Route Optimization, Load Planning, and Carrier Performance
The core of logistics management is transportation that entails the coordination of the carriers, the optimisation of the routes, and cost effectiveness. With a well-designed system, goods pass through the supply chain fast, thus avoiding delays; it is essential to the success of the supply chain management.
Warehouse Management
The proper choice of transport mode promotes cost-efficiency and assures the effectiveness and reliability of the delivery. Load planning will minimise wasteness and performance monitoring will enhance the carriers’ partnership. Such logistics approaches enhance chain management and facilitate the easier flow of products through the networks.
Space Utilization
The optimisation of storage capacity enhances the workflow. Effective use of space avoids congestion, decreases retrieval time and decreases the cost together. To learn logistics and generate optimisation of the supply distribution efforts, it is necessary to learn how to manage warehouse layout.
Picking Accuracy
Picking accuracy guarantees shipping of the right items, which minimises returns and complaints about the products. It enhances trust and simplifies the business-critical objectives of any person who strives to master principles of logistics management and institute the best practices related to warehousing.
Storage Efficiency
Accuracy and speed of goods delivery are well supported through a well-organised storage. It helps reduce unnecessary stockouts and plays a larger role in general efficient logistics management, enabling companies to adjust better to the demand and improve the use of resources and capital in the warehouse.
Material Handling
There is an influence of material handling systems on operational safety and efficiency. The correct procedures minimise losses and the effort involved. The supply chain requires businesses that concentrate on modern equipment and training to facilitate strong management logistics and an easier process in the warehouse.
Inventory Management
Proper management of inventory is also important as it makes the products accessible without exposing them to excessive stock. It facilitates proper supply chain management with proper forecasting and tracking in real-time. This component is an important issue that one has to learn in case he/she is interested in studying logistics and enhancing service reliability.
Forecasting Demand
Proper demand prediction would eliminate understocking and overstocking, which increases the profit margins. It facilitates effective procurement and production planning, which is important in ensuring an efficient logistics management structure that is fast and affordable according to the customer’s expectations.
Stock Levels
Good stock level prevents cases of not getting the products and avoids the costs of extra inventory. Stable inventory is a vital part of successful logistics so that one can timely enlarge the available assortment and reduce waste, at the same time being ready to meet unexpected requests, which can increase unexpectedly.
Safety Stock
Safety stock guards against unexpected shortages. It also provides insurance coverage against demand fluctuation and the latency of suppliers to maintain a steady customer satisfaction with the service. This will raise the level of supply chain resilience and agility in general.
Turnover Rates
Observing the turnover rates helps companies to analyse the demand for their products and adjust their purchases. High turnover is an indication of brisk business in terms of product flow, which is a vital factor towards effective logistics management and lean and efficient stocks in the supply chain system.
Technology Systems
Technology enhances the accuracy of inventory, visibility and automation. New systems such as ERP and WMS are vital to master the logistics management process in an efficient way and empower information-based choices in real-time activities of a chain management.
Order Management & Fulfilment
Order processing is optimised and leads to a better customer experience. All the processes should be precise and up to speed, beginning with order capture to delivery. The companies with good practices in this field have a high potential in logistics management as a part of the extensive supply chain complex.
Order Receipt
Effective order receiving systems verify every transaction fast and reduce errors. Promptness makes things less ambiguous and preconditions effective processing, which is crucial to any person who wants to learn logistics and enhance its implementation.
Processing
Speed and precision in processing allow orders to flow in the system without difficulties. It eliminates backlogs, decreases downtimes, and proves the efficiency of the overall logistics management system as it ensures the smooth correlation of the inventory and fulfilment teams.
Tracking
Transparency and enhancement of trust are provided through order tracking. Real-time updates make the customers happy, and they also act as a means of monitoring delays experienced by businesses. It is one of the fundamental capabilities of contemporary supply chain management, and it allows us to provide active service and quickly address concerns.
Ensuring Order Precision
Customer satisfaction is guaranteed by delivering the desired item to the perfect place. Precision in orders reduces returns and increases efficiency, which is an element of proper logistics management that directly affects reputation and cost reductions.
Freight Audit & Payment
The freight audits provide control of cost and accuracy of bills. Fixed checks and automation will eliminate errors, identify overcharges and optimise carrier payments to facilitate efficient logistics and enhanced financial cycles throughout the supply chain.
Verifying Shipping Bills
Quality control prevents expensive misjudgments and disagreements with motor freight companies. Matching of billing charges against pharmaceutical agreed rates means a business will have transparency and keep correct records- an undertaking that is required in logistics management and freight controlling procedures.
Controlling Freight Costs
Freight spend control is key towards budget discipline. Audits and negotiations can assist businesses in ensuring cost-effective transportation, enhancing the margins and assisting the leaders in learning to manage the logistics in real-time with actionable information.
Ensuring Accuracy
Freight billing helps ensure that there is trust and financial balance. Invoicing mistakes have the capacity to worsen the expenses. Strict systems of auditing play a vital role in ensuring that good standards of logistics management are maintained and in transportation processes, long-term financial health.
Key Performance Metrics (KPIs) to Track
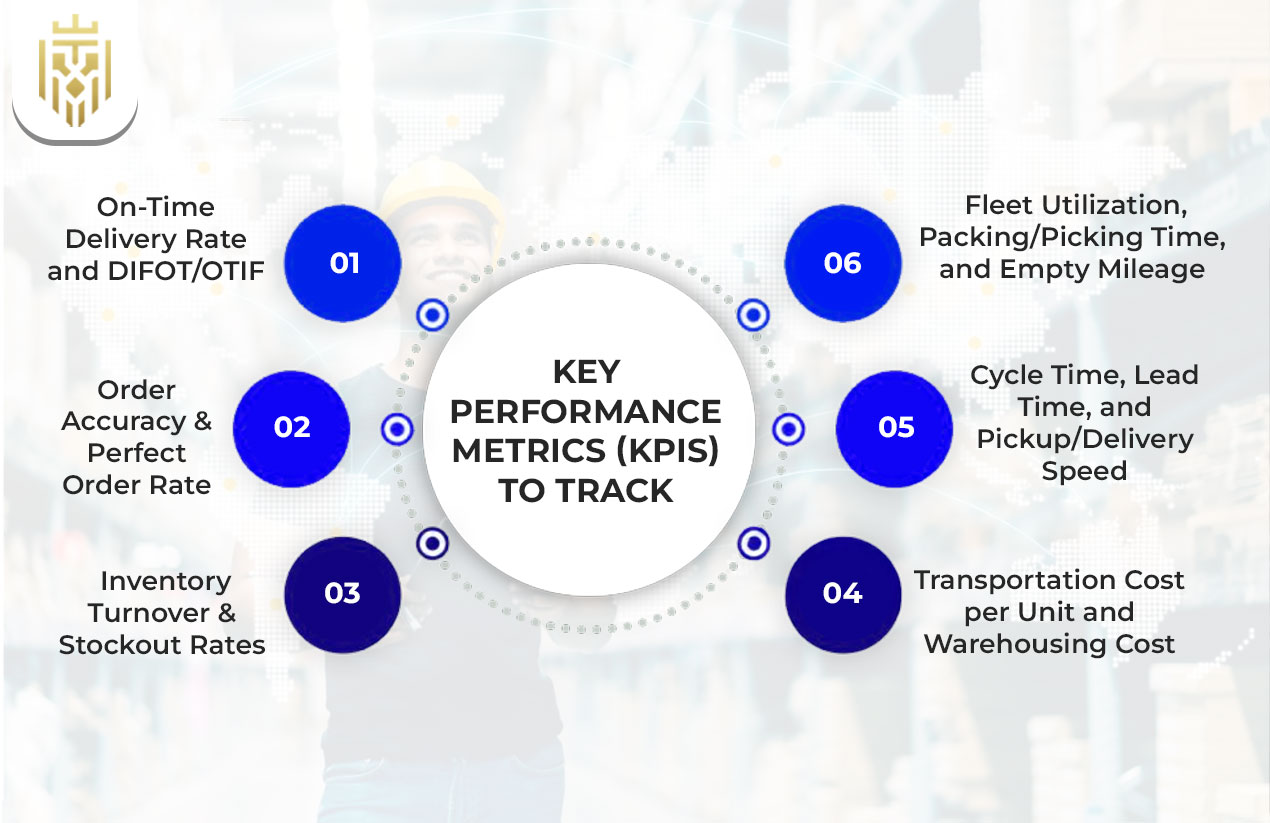
Monitoring the KPIs can tell you how effectively your logistics management system works. It provides transparency in delivery, stock levels and operational effectiveness. Keeping watch over these measures, companies might identify their weak spots and improve them in time in the general supply chain system.
On-Time Delivery Rate and DIFOT/OTIF
On-time delivery measurements and DIFOT/OTIF can be used to emphasise your punctuality. An excellent performance in this case expresses an effective chain management system. These benchmarks also point to the level of alignment of partners and internal teams to be able to deliver service expectations and delivery commitments periodically.
Order Accuracy & Perfect Order Rate
Optimal rates decrease customer complaints and waste of operations. Order accuracy tracking will allow managing logistics effectively, so the fulfilment teams can place, pack, and deliver exactly as asked, to maintain the retained customers and reduce reverse logistics.
Inventory Turnover & Stockout Rates
These measures assist the companies to regulate the quantity of stock on hand to prevent wastage or shortages. The high turnover and low stockout give evidence of an efficient supply distribution, which enhances the continuity of the services with minimal losses of items due to storage and perishable losses.
Transportation Cost per Unit and Warehousing Cost
The tracking of these KPIs will give insights regarding the efficacy of the management of the costs. Efficient logistics in management guarantees expenditure related to the value of delivery. Good control of the costs aids the overall financial well-being of transportation as well as warehousing activities.
Cycle Time, Lead Time, and Pickup/Delivery Speed
Quick delivery, less lead time, and small cycle times denote the duties of responsive logistics. These KPIs indicate customer-oriented performance to give competitive advantages in competitive markets, which is a key component of the supply chain process of today.
Fleet Utilization, Packing/Picking Time, and Empty Mileage
Better use of the fleet and cutting down on packing/picking time increases the overall efficiency. Reduced empty miles assist in reducing emissions and expenditure. Companies that want to acquire knowledge of logistics management would have to keep track of these KPIs to achieve leaner activities.
Technology & Tools Enabling Smarter Logistics
Technology is what makes logistics management smarter and faster. Whether it is tracking systems or analytics dashboards, digital tools enhance the process of decision-making, as well as automate the important processes, enabling companies to rise to the supply chain performance and responsiveness levels across the regions.
Transportation Management Systems (TMS)
TMS simplifies the routing process, eliminates the human factor, and provides transparency in tracking. The benefits they have, such as enabling efficient logistics, maximising load consolidation and maximising carrier accountability, make them crucial in the area of sustainable logistics and future development.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
WMS guarantees the actuality of the inventory, automated refilling and precise counting. It enables teams to ensure learning of logistics and decrease the errors, and facilitates synchronisation of supply chains between the demand and fulfilment.
Telematics and GPS Systems
Such systems improve the safety of a driver, reduce idle time, and comply with the route. Through enhanced monitoring of vehicle fleets, organisations apply telematics in facilitating an efficient logistics program and on-time delivery in various geographical orientations.
Data Analytics and Dashboards
Data analytics delivers business intelligence. Dashboards monitor the trends of KPIs in real-time and show the weak points and strong aspects of logistics control. Such insights will be required to learn how to manage logistics and will be utilised to drive the ongoing process improvement.
Best Practices in Logistics Management
Companies have to match their operations with technology, customer needs, and performance objectives in order to apply effective logistics. Best practices bring about resiliency, responsiveness and cost-efficiency in the supply chain management journey.
Align Strategy with Demand
Logistics measures should be based on the actual customer demands and organisational goals. Proper alignment translates to improved forecasting, planning of inventory, and reliability of deliveries, which means a more nimble and responsive supply chain model.
Optimize Routes and Inventory
Analytics help companies make smarter decisions. Route optimisation and more relevant inventory forecasting reduce waste, improve delivery times, and procure stock with the lowest carrying cost possible.
Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration
Cross-functional collaboration ensures agility and responsiveness across departments. This united front yields smoother chain management with common data findings, proactive planning, agile reaction to disruptions, and customer-specific needs.
Review KPIs & Processes
Continuous analytics will assess where the gaps are for performance. Process refinement as time goes on contributes to the effective logistics, which can help companies now required to explain ever-changing market conditions through continuous improvement.
Train Teams on Systems & Compliance
Teams know-how to guide smartly and quickly. Staffers with knowledge of logistics, applying compliance rules, and working with digital tools ensure confidence, consistency, and performance throughout the supply distribution process.
Logistics Management Challenges & Solutions
Businesses are faced with complex decision tasks daily, and so, the question of what is logistics management becomes critical to navigating these hurdles. Problems such as late deliveries, inventory imbalances, and visibility problems need to be tackled with proactive approaches and a digital transformation of the supply chain to ensure consistent performance.
Speed, Cost & Accuracy
The game of speed, accuracy, and cost is played every day in management logistics. Trade-offs have to be weighed using real-time data. If anything, logistics teams should prefer automation, route optimisation, and scalable solutions as these will allow them to provide great service on time without overspending their budgets.
Last-Mile & Demand
Last-mile delivery remains the most expensive yet unpredictable. Fleet resources and routing must be optimised while staying flexible. Smart tools and predictive analytics present the right solutions for managing this variability and reducing the risk associated with the distribution of supplies.
Compliance & Documentation
Being compliant with shipping regulations and document accuracy is what keeps delays or fines at bay. An efficient logistics management would incorporate digital document workflows within staff training and further into their daily compliance checks.
Functional System Integration
System silos restrict visibility and cause delays. Platform integration enables seamless communication between logistics, warehousing, and fulfilment. An integrated system subsequently strengthens chain management, improving coordination, reducing duplication, and fostering quicker response to customer requirements or problems relating to order fulfilment.
Disruptions & Delays
Delay disruptions and extreme weather events require agility. Organisations that master logistics and practice proactive contingency planning limit the consequences of disruptions. A combination of sourcing options and visibility in real-time provides resilience in fast-changing environments for supply chains.
A Step‑by‑Step Guide to Optimize Your Logistics Operations

Optimising begins with problem assessment and implementation of processes to circumvent them. For a company to learn logistics management, it has to rely on a data-driven approach combined with the incorporation of appropriate technology and deliberate process improvement aligned with the broader goals of supply chain management.
Audit Logistics Processes
Start by analysing existing systems and workflows. Any shortcomings must be identified in the areas of warehousing, order fulfilment, and transportation. An operational review serves as the basis for improving logistics management and points toward where performance could be significantly lacking.
Define KPIs and Benchmarks
Define key metrics reflecting business goals. Measurable KPIs promote transparency and ensure continuous monitoring toward the achievement of objectives. Benchmarking further enables teams to realise greater wins by way of effective logistics and better decision-making.
Invest in Tech & Training
Investing in tools such as TMS or WMS for the sake of visibility and having team training ensures adoption. This combination can then make the supply chain more responsive, reduce manual processes, and increase accuracy, especially when peak periods or high order volumes occur.
Pilot High-Impact Areas
Testing on a small-scale level provides feedback for real-time learning. Conducting a warehouse or route-planning pilot can illustrate potential benefits. Businesses with incremental logistics learning can scale smarter and respond faster to operational demands.
Monitor, Feedback, Improve
Track results, gather team feedback, and roll out what works. Sustainable-level improvement results from continuous upgrades. For successful logistics management, continuous learning, a feedback loop, and metric alignment form the pillars of long-term optimisation strategies.
Real-World Examples of Excellence
A startup that transcends operational excellence should be investing fully in logistics management. Real-world leaders show how good practices applied in the supply chain can be beneficial at every single touchpoint, whether this application includes automation, process innovation, or strong partnerships.
E-commerce Speed & Flexibility
E-commerce players in the game own hyper-speed shipping models and scalable fulfilment. With an automated sorting and inventory update system, these companies support efficient logistics management and, at the same time, customer satisfaction with extraordinary demand volume and tight deadlines.
Just-In-Time & Cross-Docking
Just-in-time and cross-docking approaches help reduce storage needs and streamline flows. By optimising supply distribution and reducing leakage, they enable manufacturers to respond swiftly to production demands and fluctuations in requirements without holding excess inventory.
3PL Tech Integration
The third-party logistics providers employ technology to manage different clients. With integrated systems, they improve visibility, automate billing, and scale operations. These advanced models, therefore, can give good insight into logistics management.
Conclusion
Understanding logistics management and its changing challenges is essential for staying competitive. Companies that embrace innovation, improve their operations, and meet supply chain management goals will unlock resilience, efficiency, and long-term success in their logistics networks.
FAQs
1) How is logistics management different from supply chain management?
Logistics management focuses on the smooth movement, storage, and delivery of goods, while supply chain management oversees the entire process, from raw materials to the end customer. This includes sourcing, production, logistics, and overall coordination.
2) What is logistics management?
Logistics management involves planning, executing, and controlling the flow and storage of goods from origin to destination. This ensures timely delivery, cost efficiency, and customer satisfaction within the wider supply chain framework.
3) How can logistics management help teams handle peak demand surges effectively?
Effective logistics management supports demand spikes through real-time tracking, optimized routing, flexible warehousing, and predictive planning. This allows teams to quickly scale operations while keeping delivery accuracy and resource use in check.