Understanding Transportation in Logistics
Moving goods is the core element of transportation in logistics, which can go by many names, such as movement, transfer, distribution, etc. The most evident part of logistics is that it guarantees that a product moves through the supply chain and vice versa, and it does this efficiently and safely.
Transportation has a direct effect on the success of the operation—it changes the lead time, inventory, and delivery costs all at once. The transportation of logistics has become even more critical with the increase of e-commerce and global trade and it is still a constant struggle to find the right spot between speed, cost, and sustainability.
Key functions of transportation in logistics
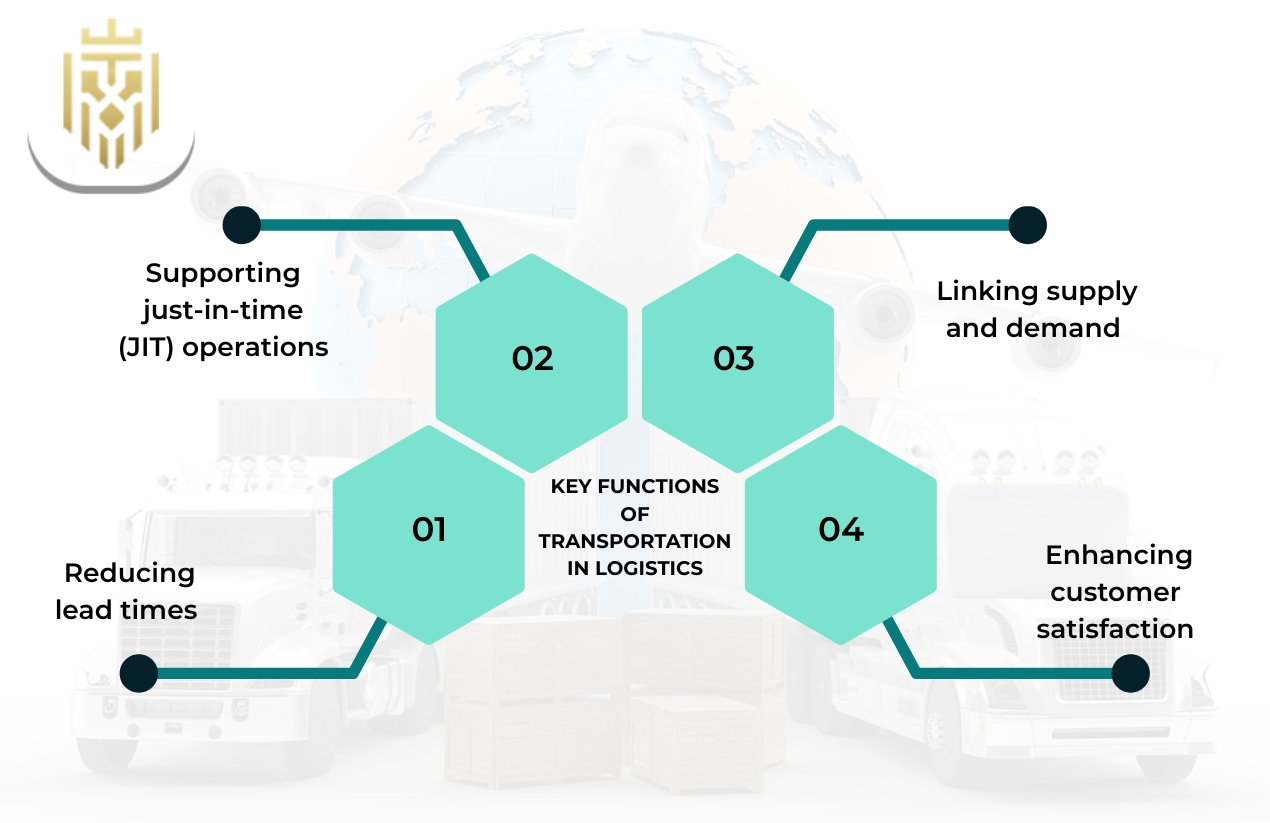
Transportation is a producer-consumer link. It allows for the efficient transfer of goods whereby the suppliers are able to offer business customers lower prices and quicker delivery besides.
Reducing lead times
Transportation plays a key role in shortening lead times by linking up different points in the supply chain with faster delivery. Efficient transportation networks keep the businesses agile while they are waiting for the market changes and the consumers’ demands.
Supporting just-in-time (JIT) operations
Transportation is the backbone of JIT and lean practices since the latter relies heavily on timely transport. So if the materials are delivered exactly when they are needed that means the production cycle is already cost-effective and there are no excess inventory pieces, which is where the whole JIT production process gets its name from.
Enhancing customer satisfaction
The customer is the king of transport, and their experience through the whole delivery process is directly linked to the transportation reliability which provides instant delivery of goods and keeping the product’s quality during transit. Efficient logistics operations allow not only to offer real-time tracking and faster service but also to build customer trust.
Linking supply and demand
Transportation plays a fundamental role in connecting supply with demand across local, national, and international markets. By linking producers with consumers efficiently, it allows businesses to expand their market reach and strengthen global trade.
Modes of Transportation in Logistics

Transportation modes taking different forms are the founding stone of logistics and supply chain management. In every case, the argument for or against a mode—be it road, rail, sea, or air—depends on the parameters of the shipment, i.e., distance, cost, speed, and the nature of the goods being transported.
Road Transport
Road transport comes first among the modes in logistics being the most popular and most adaptable. Its properties, such as providing flexible routes, door-to-door service, and almost universal accessibility, make road transport indispensable for deliveries over short and medium distances.
Benefits of Road Transport
Road transport is a mode of transport that has the best flexibility and convenience available, so it can be used to transfer goods quickly from origin to the final destination without any intermediate handling. It also plays the role of last mile delivery which is very important in e-commerce and retail. Furthermore, modern road fleets fitted with GPS and using route splicing tools contribute their share in the sunshine of unsuccessful operations’ efficiency and visibility.
Challenges of Road Transport
However, road transport is often impacted by traffic congestion, fuel price volatility, and infrastructure limitations. Driver shortages and maintenance issues can also lead to operational delays. Moreover, it contributes significantly to carbon emissions, which raises sustainability concerns.
Rail Transport
Transportation by rail is regarded as a very efficient way for the movement of goods over long distances, especially for bulk or heavy cargo. It is a backbone for the industries such as mining, agriculture, and energy, where large shipments are the rule.
Benefits of Rail Transport
The rail transport system is overall cost-effective for long-distance transportation, especially for the heavy and bulky goods. It provides better fuel consumption and lower carbon footprints when compared to the road transport. The railways also offer the safest way of transporting freight with minimized accidents and damage.
Challenges of Rail Transport
Rail transport, although it has benefits, faces challenges because of the fixed nature of the routes and the limited door-to-door service. It relies heavily on the intermodal connections with the road transport for the delivery of goods to and from the customers. Flexibility in scheduling may be limited and the slow progress in the expansion of the rail networks may also hinder the efficiency of the operations.
Maritime Transport
Maritime or waterway transport is the cornerstone of the global trade system, taking care of about 80% of the total cargo volume worldwide. It is the best way to transport huge amounts of goods from one continent to another with minimal cost.
Benefits of Maritime Transport
The shipping by sea has the least cost per ton-mile which is why it is the most preferable choice for bringing in bulk and heavy goods. The ships can carry enormous amounts from and to the world’s supply chains which range from raw materials to manufactured goods. The shipping of goods by sea also comes with many containerised solutions that cover the cargo during the long sea transit.
Challenges of Maritime Transport
On the other hand, maritime logistics is the slowest among transportation methods. The shipping process is highly dependent on port facilities and can be disrupted by a number of factors such as bad weather, customs delays, and traffic jams. The rising fuel prices and the environmental regulations are extra difficulties for the shipping companies to operate.
Air Transport
Air transport is the quickest way in logistics, appropriate for high-value, time-sensitive, or perishable goods. It brings fast global connectivity and also underpins industries like pharmaceuticals, electronics, and fashion, where speed is a must.
Benefits of Air Transport
Air freight offers the shortest transit times, perfect for urgent deliveries and just-in-time supply chains. It gives very high reliability, little handling, and more safety against theft or damage. Furthermore, it supports international trade by connecting even the most distant markets within hours.
Challenges of Air Transport
Hefty prices and limited cargo capacity are air transport’s major downsides. Also, strict regulations, airport overcrowding, and bad weather can cause delays in pipeline delivery. High fuel consumption is one of the reasons air logistics are not considered sustainable and raises environmental issues.
Intermodal and Multimodal Transport
Intermodal and multimodal transport are strategic methods that combine several modes in order to get the best efficiency, cost control, and flexibility.Intermodal transport works by using standard containers throughout rail, road, and sea without direct handling of cargo, thus minimizing damage risks and maximizing the time of transition.
While multimodal transport is done under a single contract covering all the different types of transport, so that there is good communication and responsibility throughout. These systems improve dependability, facilitate the movement of goods across borders, and assist companies in minimizing their expenses and at the same time improving their eco-friendliness.
Factors Influencing the Type of Transport

Selecting the appropriate mode of transportation requires a detailed understanding of various influencing factors. Businesses consider these parameters to ensure operational efficiency, cost savings, and timely deliveries.
Distance
Distance is always one of the chief factors. Local shipments that do not exceed a few hundred kilometers within one state or city are normally moved by trucks, while the international shipment going to the other side of the world may opt for rail, sea, or air depending on cost management. The longer the journey, the more vital it is to manage the factors of speed, cost, and load capacity in a way that will be most effective for the transport.
Speed and reliability
The businesses selling and trading with fast-moving goods like food or in-demand products are always looking for the quickest way and, at the same time, the most reliable one. The air and road transport will deliver the products quickest, while the sea and rail will be the cheapest but the slowest. Choosing the right transport mode helps companies to keep their deadlines without sacrificing either quality of service or cost efficiency.
Cost considerations
Cost effectiveness is one of the decisive factors in logistics operations. Air transport is fast but costly. Sea and rail are cheaper options for goods that are not time-sensitive or in bulk, which helps companies to balance cost and service. When assessing the total logistics costs, which will include fuel, labor, and handling, it is easier to arrive at the most economical transport option.
Nature of goods
The transport choice is determined by the type of goods, their weight and, mainly, their sensitivity. The products that are fragile, perishable, or high-value need to be transported only through air and that too under secure and speedy conditions while durable and bulk commodities may be transported by rail or sea. The proper mode selection based on product characteristics ensures that there is minimal damage and optimal handling throughout the transit.
Infrastructure availability
The availability of infrastructure like roads, ports, rail networks, and airports directly impacts transportation efficiency. Countries with advanced logistics infrastructure benefit from smoother movement, reduced transit time, and lower operational costs. Poor infrastructure, on the other hand, can lead to delays, higher maintenance expenses, and reduced overall reliability.
FAQs
1) What is the most cost-effective mode of transportation in logistics?
The most affordable way to transport long-distance and large-volume goods is through maritime transport per ton-mile because it has a very low cost and comes with huge capacity. Thus, it heavily relies on global trade where time plays a lesser role than cost and thus, cost is prioritised. Besides that, it also promotes eco-friendliness by consuming less fuel per cargo unit.
2) How do logistics companies decide which transport mode to use?
Logistics service providers evaluate the factors of shipment type, distance, urgency, and cost constraints for selecting the most appropriate transport mode. A lot of companies have started to use sophisticated software and TMS (Transportation Management Systems) for assessing the options and forming the hybrid transport plan aimed at achieving maximum efficiency.
3) What role does packaging play in logistics transportation?
Packaging acts as a shield for goods throughout their journey and provides protection against damage, contamination, or theft. Furthermore, it is a significant factor in determining the load efficiency and compliance with international standards, especially in case of air and ocean shipping. The use of strong and sustainable packaging not only eliminates waste but also increases the effective usage of space.
4) How does technology improve transportation efficiency?
The use of modern technologies such as GPS tracking, IoT sensors, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and digital freight platforms has changed the face of logistics transportation. The adoption of these technologies leads to the provision of real-time tracking, predictive maintenance, automated scheduling and fuel optimisation which, in turn, leads to faster and more environmentally friendly deliveries.
5) How do environmental concerns affect logistics transportation choices?
With growing focus on sustainability, businesses are adopting cleaner fuels, electric fleets, and multimodal solutions to reduce carbon emissions. Green logistics practices such as route optimisation, energy-efficient ships, and eco-friendly packaging are shaping the future of transport decisions.