Understanding Product Inventory
Product Inventory is the total stock that a business keeps either to sell directly or to use in manufacturing other goods. This includes everything starting from raw materials to finished product inventory ready for customers. Product Inventory is the backbone for E-Commerce and manufacturing companies. To maintain the best marketing campaigns and customer service efforts, it is essential to have a well-managed product inventory.
Apart from tracking numbers, a good Product Inventory System offers insights into supply chain efficiency, demand trends, and overall profitability. Whether you are running a small scale operation or manage global distribution, keeping an accurate data on what you have and what you need enables smooth and effortless operations.
What Can Smart Inventory Control Do for Your E-Commerce?
Smart Inventory Management is a game changer for E-Commerce businesses. Having a smart inventory is not about having products on shelves, it’s about ensuring that the right product is available at the right time in the right accurate quantity. Smart Inventory makes sure that the business is prepared for demand spikes, whether its a festive season or flash sale, without over loading your storage. It plays a vital role in order fulfillment. While avoiding back orders it helps in reducing the risk of delivering incorrect items. Furthermore, smart systems help to monitor sales trends, identify bestsellers, and plan restocks in advance. Eventually, better control over stocks leads to better business
Inventory in Action
Inventory management directly impacts customer’s perception towards a business. The journey from procurement to delivery depends on keeping your stock levels aligned with the actual demand.
Turning Stock into Service
When a customer orders a product, they expect it to be available and delivered on time. That’s when the inventory transforms from storage rooms to real service promise. Effective product inventory management always ensures that sales are backed with actual stock, avoiding delays and any cancellations. While treating stock as a customer service tools, businesses can enhance loyalty and strengthens their brand reputation.
Boosting Customer Trust
Trust is fragile, once broken, it’s hard to regain, it needs to be handled sensitively. For a business, customers’ trust is significant. If a product ordered by customers is out of stock due to which it got delayed or cancelled, they will likely turn to competitors. Hence, keeping product inventory updated in real time is crucial, it eliminates the risk of misleading product availability and ensures that every order is fulfilled as promised.
Elevating Supply Chain Flow
Product Inventory is a link to a broader supply chain. Well managed stocks makes it easy for warehouses to process orders quickly, suppliers to deliver on time, and distributors to operate without obstacles. This seamless flow helps in reducing lead times and support faster market admiration.
Keeping Costs in Check
Each warehouse unit has a cost, not just purchase value but for storage, handling and potential depreciation. Overstocking ties up capital and may sometimes lead to wastage spoiled goods, whereas understocking means lost sales. A balanced approach to stock management allows you to keep operations smooth and profitable.
Tracking via EOQ & ABC Analysis
Economic Order Quantity is a formula used in Inventory management to manage the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs, specially the costs of ordering and holding inventory. On the other hand, ABC analysis is a technique where stocks are categorized into three groups based on their importance. “A” for high value items, “B” for mid-value, “C” for low-value items. These tools helps to ensure you invest resources where they matter most.
Measuring DIO and Stock Performance
Also known as Days Sales of Inventory (DSI) or Days in Inventory (DIL), DIO stands for Days Inventory Outstanding that measures how long, on average, it takes for your inventory to be sold. A lower DIO signify as faster turnover and healthier cash flow. Measuring DIO allows businesses to spot inefficiencies and make informed decisions about procurement and sales strategies.
Hallmarks of Intelligent Inventory Tools
Now-a-days leading businesses count on smart systems to manage their inventory, replacing manual spreadsheets with data-driven and automated platforms. These intelligent tools not only track stock but also help predict demand, avoid stock shortage, and upgrade storage.
Reordering with Alerts & Automation
Automation guarantees you never miss a refilling window. Smart systems are set to send alerts or automatically generate purchase orders when stock level is declining before a predefined zone. This helps in reducing the risk of human oversight and makes sure that the customers requirements are getting full filled.
Across Multiple Sites
If a businesses regulate warehouses or outlets in numerous regions, tracking stocks across all the sites is a difficult task. Therefore, using AI tools reduces half of your stress. It collects data from every location and gives you a clear view in single and overall stock health.
With Live Updates Everywhere
No matter wherever you are, in the office or travelling, the live inventory updates helps you to make a quick, and cognizant decisions. For example, if a warehouse is low on stock, you can organize urgent transfers from another location.
Running Everything from One Dashboard
Rather than juggling in multiple systems, a centralized dashboard provides real time insights into trends, incoming shipments and outgoing orders. This smart move can reduce any sort of complications and helps you spot issues before they become a problem.
Plug-and-play with ERP & MRP Systems
Integrating ERP (Enterprise Resources Planning) and MRP (Manufacturing Resource Planning) systems confirms that inventory data is automatically shared across procurement, sales and production teams. This helps in keeping everyone aligned and also minimizes the risk of delays that may occur due to miscommunication.
Inventory Classification
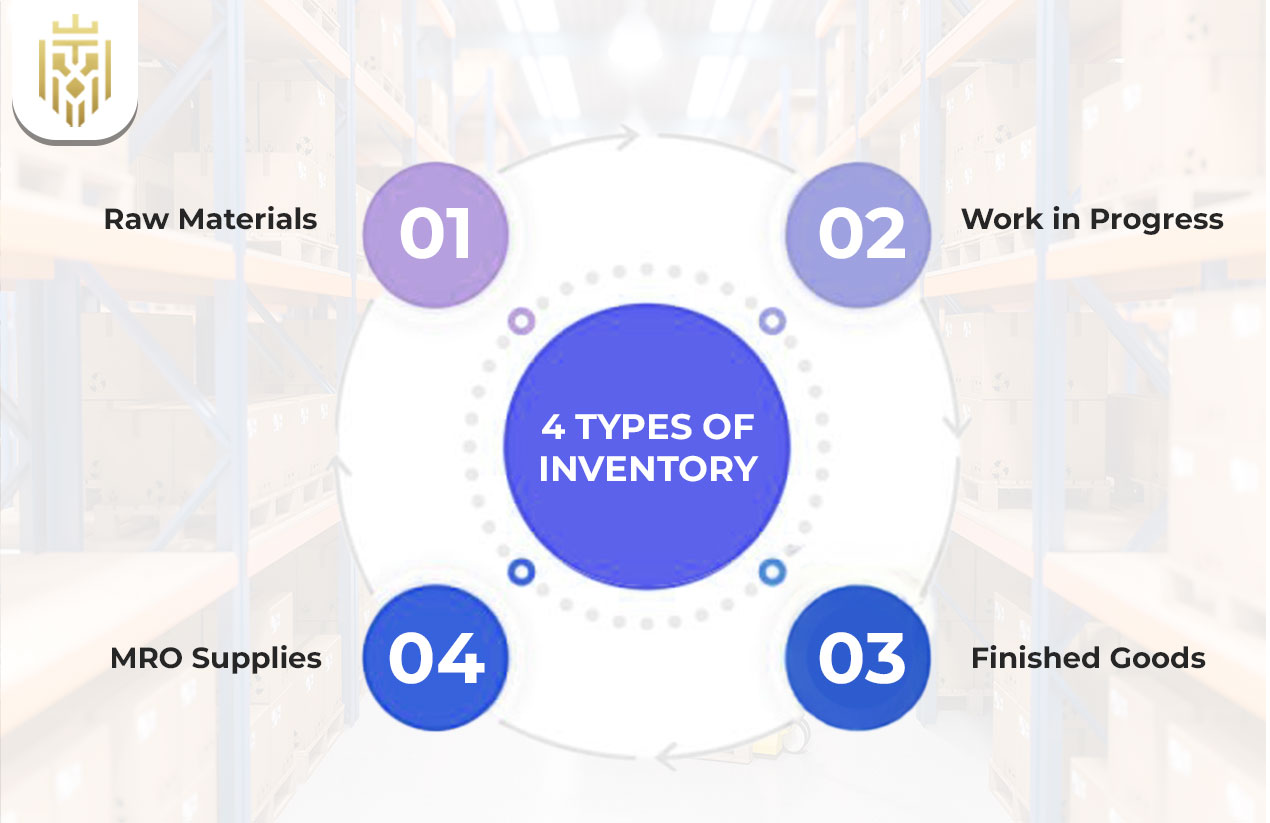
Inventory is a vast term, not all inventory is the same. Understanding its classification is very important to manage the business effectively.
Raw Materials
Raw materials are one of the basic inputs required to produce finished products, such as fabric for clothing, manufacturers or steel for construction organizations. Managing raw material efficiently ensures production schedules met without any interruptions.
Work in Progress (WIP)
Work in progress (WIP) indicates the unfinished or partial finished goods that are still in the manufacturing process. Tracking down WIP help businesses identify blockages in productions and improve throughput times.
Finished Goods
Finished Goods are the products that have completed the manufacturing process and are ready for sale. Finished product inventory must be carefully monitored to meet customer demand without overstocking.
MRO Supplies
MRO Supplies stands for Maintenance, Repair and operations supplies, these are the unsung heroes of business stability.These include cleaning products, spare parts and other items necessary to run operations smoothly.
Must-Know Inventory KPIs

Monitoring KPIs enables businesses to calculate the efficiency of their inventory strategies and make adjustments for better results.
How Often Inventory Turns Over (Turnover Ratio)
Inventory Turnover ration measures how many times inventory is sold and replaced within a certain timeframe. A high turnover ratio usually reflects strong sales and efficient stock management, while a low ratio may signals overstocking or weak demand.
Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO / DSI)
Businesses aim for a balance, too low in stock might mean frequent stock outs, while too high ties up valuable capital. DIO or DSI measures the average number of a product stays in the stock before it’s sold.
Order Accuracy Scores
Order accuracy scores how often customers’ orders are full filled without errors. High accuracy means petty returns, better customer reviews and improved operational efficiency.
Stockout Percentages
Stockout percentage tracks the number of products unavailable when customers want to buy it. Lowering this measure is essential for keeping your customers happy and maximizing revenue.
Real-World Inventory Headaches
Inventory management is not a piece of cake, even with technology, you might sometimes face obstacles that require strategic solutions.
Avoiding Overstock vs. Empty Shelves
Having a balance between supply and demand is tricky. Overstocking may result in wasted spaces and capital, while empty shelves may push customers to competitors. So, to avoid these business must constantly refine forecasts to stay prepared for every situations.
Streamlining Warehouse Chaos
Unorganized warehouse can cause delays, misplaced products, and incorrect shipments. Implementing clear labeling systems, entitled storage areas and efficient picking methods can tremendously improve speed and accuracy.
Replacing Paper Trails with Precision
Manual, paper-basedsystems are liable to errors and slow processing. Thus, switch to digital tracking solutions that reduces mistakes, it improves reporting, and enables real-time visibility.
Fighting Hidden Costs in Indirect Spend
Indirect procurement refers to buying items not directly tied to production. This can silently drain budgets if not tracked. Centralizing these purchases and monitoring supplier contracts helps keeping expenses under control.
FAQs
1) What is product inventory?
Product inventory refers to the stock of goods a business has on hand, either for sale or for use in production.
2) What types of inventory exist in businesses?
In businesses main types of inventory are raw materials, work in progress, finished goods, and MRO supplies.
3) What does indirect procurement mean?
Indirect procurement refers to purchasing items not directly used in production but necessary for operations, such as office supplies or cleaning materials.
4) What are the challenges of managing indirect procurement?
Challenges of managing indirect procurement include lack of visibility, inconsistent suppliers, and difficulty in tracking expenses.