What Is Demand Planning?
Demand planning is a critical supply chain process that involves analyzing historical data, market trends, and other factors to anticipate future needs, allowing businesses to optimize inventory levels, procurement strategies, and production schedules. Productive demand planning helps businesses reducing costs associated with excess inventory or stock outs, ultimately improvising profitability.
In today’s expeditiously moving business environment, demand planning plays a crucial role in responding to changeability, be it sudden demand surges or supply disruptions. Regularity in alignment across departments ensures stakeholders stay connected and responsive to real-time market developments.
What Does Demand Planning Involve?
Demand Planning involves various factors, starting with gathering historical sales data, market intelligence, and behavioral insights to form a comprehensive view. These data points work as statistical models and human judgment to create accurate forecasts.
Key Components of Demand Planning:

- Forecasting: Forecasting means using historical, statistical models, and market trend analysis to predict future demand.
- Data Analysis: Data Analysis involves collecting historical data of sales, market trends, customer feedbacks, related information, and analyzing it.
- Collaborative Planning: Collaborative Planning involves various departments like sales, operations, and marketing to gather insights and ensure alignment.
- Scenario Planning: Preparing for multiple possible scenarios that might impact demand, like economic downturns or changes in consumer preferences called Scenario Planning.
- Supply Chain Alignment: Coordinating forecasts with production, inventory, and distribution plans.
- Strategy Integration: Strategy Integration refers to using demand forecasts to inform business strategies, capacity planning, and other key decisions.
- Continuous Review: A regular update in forecasts based on real time data and market changes is called as continuous review.
Who Is Responsible for Demand Planning in an Organization?
Demand Planning moves alongside with supply chain or operations function, as they are the one’s who oversees inventory and fulfillment. Although it also includes sales input, marketing, and financial data to ensure predictions are realistic and aligned with the business goals. In most companies, a dedicated demand planner or planning team collaborates with these contributions, acting as the bridge between departments, so everyone works from the same demand outlook.
How Does Demand Planning Differ Across Industries?
Demand planning varies according to different industries:
- In fast moving consumer goods (FMCG), demand planning must adjust to explosive promotions and a very short lifecycle.
- In manufacturing and industrial environments, long lead times and supply complexity require higher accuracy of forecasting and buffer planning.
- Retail demand planners face challenges such as omni-channel demand, returns, and predictive sizing.
- High-tech and fashion sectors wrestle with unexpected trends, introductions of new products, and shorter lifecycle timelines, making flexible, scenario-based planning important.
- In all sectors, however, the core demand planning is the same that is, historical data, forecasting models, and cross-functional alignment; these things are applicable in various kinds of industries.
Why Businesses Can’t Ignore Demand Planning
Demand Planning is an essential part of business, ignoring it means affecting operations, inventory management, and ultimately, profitability. By accurately forecasting demand, companies can improve inventory levels, decrease wastage, reduce costs, and optimize customer satisfaction.
Why Is Demand Planning the Backbone of Efficient Supply Chains?
Demand planning ensures that every link in the supply chain functions effectively and efficiently. Accuracy in demand can forecast support inventory optimization, reduce costs of holdings, and safeguard against stock outs.
These forecasts allow informed decisions around procurement timing, production capacity, and distribution logistics, which helps the organizations to allocate resources when and where they are need the most. Apart from this, demand planning improves dexterity by continuous forecasting update with real-time data, with the help of which businesses can respond to turmoil, demand spikes, or supply issues faster and more accurately.
How Demand Planning Is Different from Forecasting?
Although Demand Planning and forecasting are often used as similar term, it has a critical distinction. Forecasting is the statistical or judgmental prediction of future demand, whereas Demand Planning goes beyond. It covers forecasting, collaborating, strategy, and execution. Planners ensures that comes into action, aligned plan across functions.
Forecasting mostly focuses on a shorter timeframe, be it weeks or months. Demand Planning, on the other hand, is more long-term and flexible. It encircles a wide timeframe, either months or years, and it needs regular adjustments to adapt to the shifting market conditions.
To sum up, forecasting feeds demand planning, but demand planning is where value is unlocked through buy-in, strategy alignment, and execution.
Can Demand Planning Minimize Wastage and Overstocking?
Indeed, Demand Planning minimizes wastage and overstocking. Better forecast accuracy means companies can carry leaner inventory, reducing storage, destruction, and tied up working capital. A 15-point improvement in forecast accuracy can make a reduction in, free up cash, and imp improve profitability. Reducing waste goes alongside with delivering customer satisfaction through better availability, creating a direct win by both serving customers and improving financial health.
What Happens When Demand Planning Fails?
Indeed, Demand Planning minimizes wastage and overstocking. Better forecast accuracy means companies can carry leaner inventory, reducing storage, destruction, and tied-up working capital. A 15-point improvement in forecast accuracy can make a reduction in, free up cash, and imp improve profitability. Reducing waste goes alongside delivering customer satisfaction through better availability, creating a direct win by both serving customers and improving financial health.
Core Steps in Building a Strong Demand Planning Cycle
To build a strong demand planning cycle a business needs to follow a certain repeated rhythm. This starts with gathering clear data, forecasting with the right methods, aligning plans with capacity, then monitoring and refining it. Every step informs the next, building accuracy and organizational trust. The aim isn’t to have a perfect anticipation, it is an active learning process. Over time, this cycle becomes a competitive advantage.
Gather Historical Sales and Market Data
Begin with clean, integrated data—sales history, inventory levels, marketing campaign results, and external economic indicators. Data silos and incomplete information undermine forecasting quality.
Choose the Right Forecasting Models
Choosing the right forecasting models is also an important aspect of building a strong demand planning cycle. A perfect model of forecasting is using a blend of quantitative models (time-series, regression, machine leaning) and qualitative insights (sales input, market trends, executive judgment). Intelligent methods like AI can improve forecast accuracy significantly.
Align Forecasts with Operational Strategy
Once forecasts are already generated, incorporate them with supply chain, procurement, finance, and marketing, aligning capacity, inventory buffers, and budgets.
Collaborate Across Departments
Have regular forecast review sessions to ensure conformity. Cross-functional stakeholders should be involved in demand planning to align perspectives, eliminate biases, and create consensus.
Adjust for Seasonality and Market Trends
Productive demand planning accounts for seasonal fluctuations and dynamic market trends, helping businesses optimize inventory, reduce risks, and meet customer needs frequently.
Track, Refine, and Reforecast Frequently
Demand planning is cyclical. Continuously measure forecast accuracy, learn from variations, and apply adjustments. Repeated refinement improves reliability over time.
Key Components That Shape Demand Planning
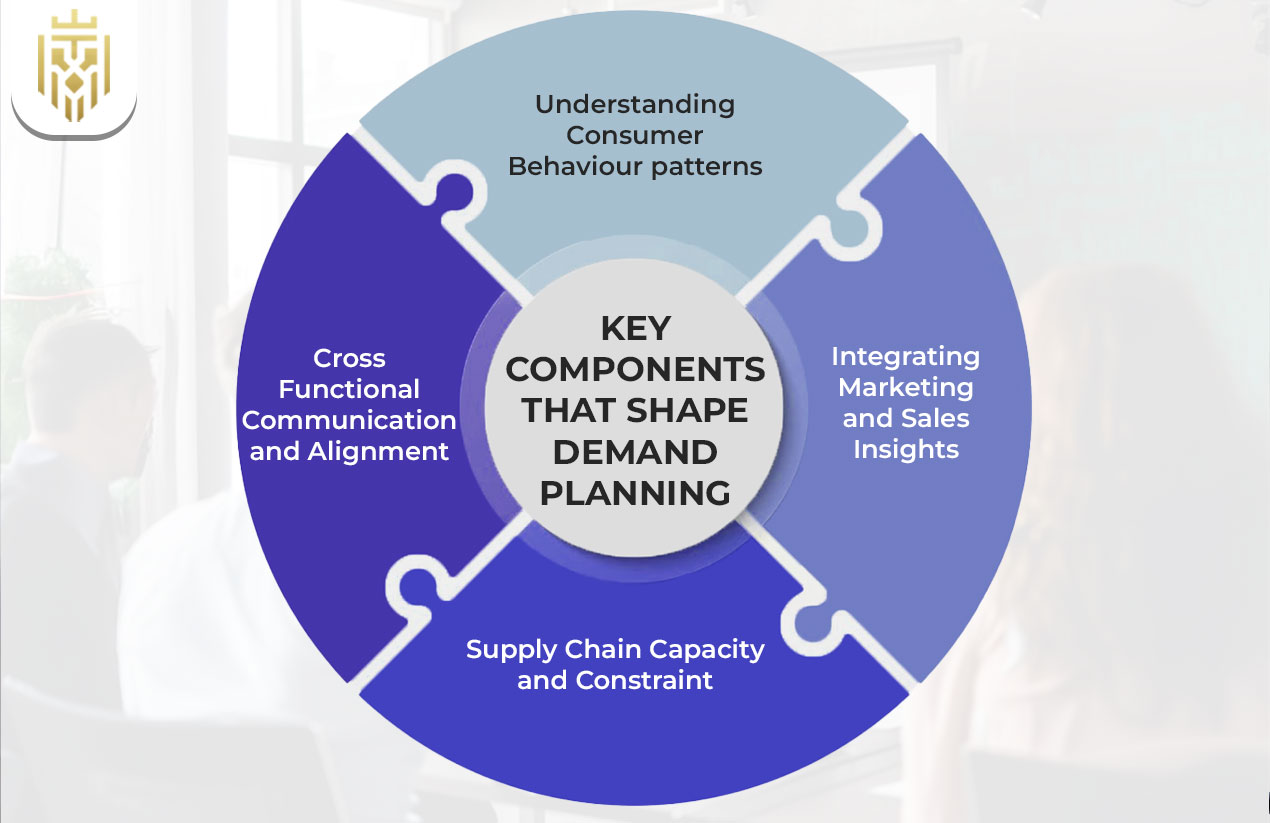
Beyond process, there are a few elements that shape the demand planning. Customer behavior, marketing and sales inputs, supply constraints, and cross-functional alignment. These are the components that ensure the forecast reflects reality. When these elements are well-linked and transparent, planners can built forecasts that are both realistic and profitable. If they are missed, forecasts accuracy can drop rapidly, resulting in costly mistakes.
Understanding Consumer Behavior Patterns
Understanding consumer behavior patterns is essential for businesses as it helps planners to predict how individuals will make purchasing decisions and shape their marketing strategies accordingly. This includes studying different factors that inspire customers, like psychological, social, cultural, and personal influences, to understand their desires and buying patterns.
Integrating Marketing and Sales Insights
Product launches, marketing campaigns, and sales promotions can drastically hamper demand. Planners must integrate input from revenue generating teams to indicate true intentions.
Supply Chain Capacity and Constraints
Understanding production leading times, supplier reliability, and logistics limitations helps planners to create realistic plans that can be delivered without over promising resources.
Cross-Functional Communication and Alignment
Regular synchronization between the supply chain, sales, finance and operations are crucial. Shared dashboards, clear timelines, and common language helps team work collaboratively.
Tools and Technology That Power Demand Planning
Modern demand planning runs on technology that makes data timely and decisions actionable. AI and predictive analytics improve forecast accuracy, while real-time dashboards surface exceptions early. Cloud platforms connect teams and systems, and mobile access keeps planners responsive on the go. Together, these tools compress reaction time and elevate outcomes.
Role of AI in Forecast Accuracy
AI and machine learning enhances forecasting by detecting complex patterns, adjusting for variations, and learning from real time data, a major upgrade over classic statistical models.
Real-Time Dashboards and Data Feeds
Regular clarity into inventory, sales, and supply statuses allows planners to react quickly to changes, reducing lag and enhancing acceptance.
Use of Cloud-Based Demand Planning Solutions
Cloud platforms allow scalable, and integrated tools, connecting teams across geographies with shared data and unified.
Predictive Analytics and Scenario Modelling
Predictive Analytics and scenario modelling helps to inspire outcomes under different market scenarios, allowing planners to test risks, promotions, and supply disturbances proactively.
Mobile Access and On-the-Go Adjustments
Mobile enabled planning tools allow managers to make timely decisions even while not being in the office, crucial during fast-paced situations.
Enhancing Demand Planning with Strategic Techniques

Once the basics are in place, strategy raises high. Demand sensing adds near real-time signals, probabilistic forecasting quantifies uncertainty, and IBP links plans to financial outcomes. Alignment with the promotions and building risk scenarios ensures the plan holds under stress. These techniques turn a good process into resilient one.
Incorporate Demand Sensing for Better Agility
Demand sensing uses near real-time data to detect early shifts in demand, sometimes providing quicker responsiveness than classic and traditional forecasting.
Leverage Statistical and Probabilistic Forecasting
Uncertain models deliver ranges rather than a single point forecasts, that helps planners understand variations and plan for possibilities.
Align Demand Planning with Promotional Campaigns
Demand spikes around marketing activities needs close simultaneous occurrence, that align production inventory, and logistics with campaign timing.
Use Integrated Business Planning (IBP)
Integrated Business Planning extends planning by combining financial, strategic and operational planning, that ensures full organizational alignment.
Include Risk and Contingency Scenarios
Plan for external disruptions, supplier delays, geopolitical events, or demand shocks with scenario based modeling and repetitive planning.
Demand Planning Applications Across Business Functions
The forecast isn’t just for planners—it powers decisions across the business. Procurement times buys and buffers, S&OP matches demand with capacity, finance aligns budgets and cash flow, and CX teams promise realistic SLAs. When every function works from the same demand signal, execution becomes faster, cheaper, and more consistent.
Inventory and Procurement Teams
Demand Planning informs purchase timing, buffer levels, and reorder quantities helping procurement act with confidence and minimize stocks risks.
Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP)
Demand planning feeds into the S&OP framework—a collaborative monthly cycle aligning forecasts with production, finance, and strategic goals.
Finance and Budgeting Teams
By providing accurate demand forecasts, finance can better plan budgets, cash flow, and capital allocation—driving improved financial performance.
Customer Experience and Service Optimization
Reliable demand planning ensures products are available in full and on time, reducing back orders and improving customer satisfaction.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Demand Planning
Even mature teams stumble on familiar traps: leaning only on history, planning in silos, overlooking external forces, and failing to replan in real time. Each erodes accuracy and confidence in the forecast. The remedy is simple but disciplined—integrate signals, collaborate routinely, and measure/adjust frequently. Small fixes here pay outsized dividends.
Relying Solely on Historical Data
Purely depending on historical models can miss new trends, promotions, or market shifts. Demand planning must combine both data with market insight.
Ignoring Cross-Department Collaboration
Ignoring collaboration between marketing, sales, finance, and operations can results in inaccurate forecasts, misaligned goals, and supply chain inefficiencies in demand planning.
Underestimating External Market Forces
Inadequate consideration of factors like economic shifts, competitor strategies, or changing customer behavior can reduce the strength of demand forecasts and disrupt overall business planning.
Lack of Real-Time Adjustments
Without constant monitoring and updates, forecasts became outdated and inaccurate, especially during disruptions. Demand planning must adjustable & dynamic, not static.
FAQs
1) What is Demand Planning?
The process of forecasting customer’s demand and aligning inventory, production, and supply chain operations to meet it efficiently is called Demand Planning. It is a combination of data analysis, forecasting models, and cross functional collaboration to ensure products are available when and where customer need them.
2) How does Demand Planning work?
Demand Planning works by gathering historical data, market trends, and input from different departments, using forecasting methods to predict demand, and then integrating those prediction into operational strategies. The process repetitive, with frequent adjustments based on new data and market changes.
3) What are the key differences between Demand Planning and Forecasting?
Forecasting is all about predicting future demand using statistical or judgment based procedures. Demand planning takes forecasting further by incorporating it into a collaborative, strategic process that aligns all business functions with the forecasts.
4) Why is Demand Planning critical for business success?
Demand Planning is critical for business success because it prevents stockouts and overstocking, optimizes resources, reduces waste and ensures a smooth supply chain. Businesses that use demand planning effectively are more rapid and strong in responding to market changes.
5) Which industries benefit most from demand planning?
Demand Planning is beneficial for different types of industries, but it benefits especially those with changing demand, long lasting times, or seasonal trends, like FMCG, retail, manufacturing, fashion, and high-tech sectors.
6) How does technology help in improving demand planning?
Technologies like machine learning, AI, cloud platforms, and real time dashboards helps in enhancing forecast accuracy, improve data visibility, and enable faster responses to market changes.
7) What are the common challenges in implementing demand planning?
Some of the biggest challenges in implementing demand planning are poor quality, inadequacy of cross- department collaboration, over confidence on historical data, and failing to update forecasts regularly.
8) Can AI replace traditional demand planning methods?
AI can greatly influence demand planning by identifying patterns and adjusting forecasts in real time, but it works perfect when incorporated with human expertise and cross-functional insights.
9) How often should forecasts be revised in demand planning?
The Best method is to review and adjust the forecast on a monthly basis, but high unpredictable industries may require weekly or even daily updates.
10) What tools are used for effective demand planning?
Common tools used for effective demand planning include AI-driven forecasting platforms, ERP systems, cloud-based demand planning software, real-time dashboards, and predictive analytics tools.