What is Dead Freight?
Dead freight is a situation where a charterer has booked shipping space but does not occupy it to full capacity, resulting in empty space which has to be paid for. When it comes to maritime trade, knowing what is dead freight in shipping is critical in preventing costly errors.
Who Covers Dead Freight Costs?
The financial burden of dead freight is usually on the charterer. Shipping agreements are frequently accompanied by a clause in the contracts where unused space is chargeable to ensure that vessel owners are paid based on the scheduled part of the trip that was not used.
Tips for Shippers to Stay Ahead
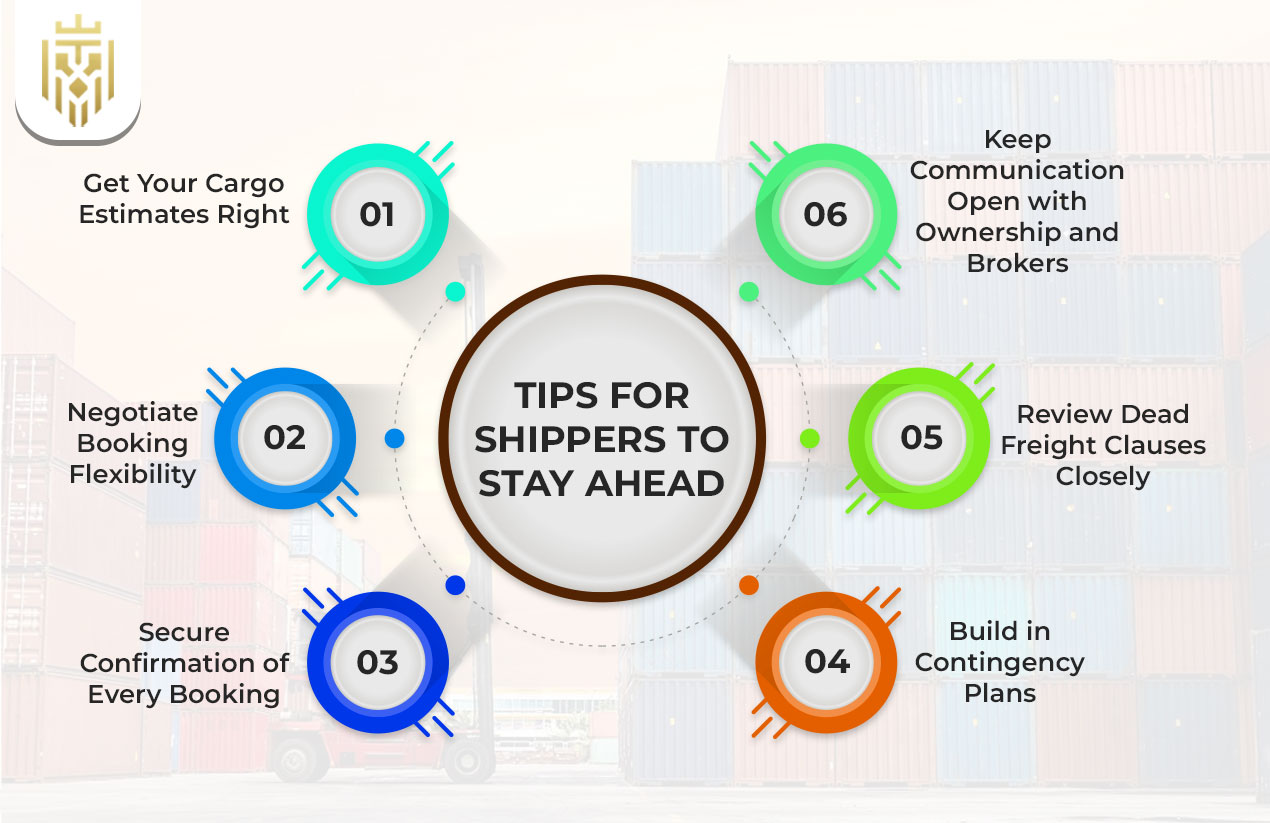
Mitigating dead freight involves shippers improving cargo forecasting, revisiting contract conditions, and communicating effectively with partners in the chain of supply. Strategic planning not only minimises cost risks but also creates business credibility across competitive freight markets.
Get Your Cargo Estimates Right
The initial defence against dead freight charges is an accurate cargo estimate. The excess capacity caused by overbooking space in dry bulk or containerised freight can result in needless expenditures and margins on unused capacity, which directly hurts operational profitability.
Negotiate Booking Flexibility
Under variable freight demands, flexible booking terms help guard against unexpected demands for shipping volume. This method enables flexibility without violating contractual agreements, costs are predictable, and the relationship with ship owners is healthy.
Secure Confirmation of Every Booking
Carriers must always confirm your booked space in writing. This guarantees that all shipping contracts are officially recognised so that you are not subject to controversy and that there are no false assumptions that might result in dead freight penalties.
Build in Contingency Plans
Solid contingency planning in shipping also considers last-minute alterations in demand or route or cargo shortages. Such methods reduce disruption to operations and ensure that committed freight capacity will be used efficiently.
Review Dead Freight Clauses Closely
It is important to look through the dead freight clauses in the contract documents carefully. To prevent unforeseen financial liability, seek explicit definitions, exceptions, and details of cost liability, particularly in dry bulk charter agreements.
Keep Communication Open with Ownership and Brokers
Open communication with the shipowners and charterer brokers can solve capacity problems before any development. Advance negotiations tend to avert breach of contract and allow for speedy changes in terms of shipment.
Steps to Calculate Dead Freight

Dead freight is calculated based on accurate data about actual and booked quantities of loads, agreed freight rate, and possible corrections. This guarantees proper financial settlements in seaborne cargo movements.
Identify Contracted Cargo
Dead freight is calculated based on the contracted volume of cargo. The overestimation approach can increase costs in dry bulk shipping, whereas the underestimation risks leave space underutilised. Proper volumes save not only the freight budgets but also the operational efficiency of a charterer, so deep, accurate volume planning is a central task of every charterer in maritime transport.
Record Actual Cargo Loaded
This figure indicates the real cargo loaded physically onboard. Ranking disparity between contracted and loaded quantities may lead to dead freight charges, especially when cargo is shipped in high volumes. Regular monitoring and reporting among the shipper, broker and charterer minimises mismatches and losses in the international freight transactions.
Calculate Unused Volume
Delivery deviation is calculated by deducting the actual delivered quantities from the contracted cargo amount. This spare capacity directly results in dead freight liabilities in dry bulk shipping. Such waste can be mitigated through proper planning, real-time monitoring, and aggressive coordination, which safeguards the profitability of operations during the shipping process.
Apply Agreed Freight Rate
The financial effect of unused capacity is directly proportional to the agreed freight rate per tonne or cubic meter. Concerning charterer agreements, even a small rate variation can have a crucial effect on dead freight expenses, and rate negotiations, as well as specific booking commitments, are essential to the cost management of maritime shipping and bulk transport contract agreements.
Use Formula or Fixed Rate
There are shipping contracts that use fixed-rate calculations and formulas that use real volumes of cargoes loaded compared to contracted loads. The applicability of any of the methods is crucial to charterer operations, as dead freight settlements are determined accordingly, preventing disputes and fully complying with contractual obligations.
Review Charter Party Terms
The charterer must consult the charter party about specific dead freight clauses. These terms can encompass exceptions, calculation procedures and limits (particularly with respect to dry bulk freight activities), assisting in avoiding contractual disputes and having understandable expectations for both parties to a shipping transaction (vessel owners and shippers).
Ship Rope
Ship Rope provides analytics, real-time cargo management, and real-time tracking to shipping professionals. These tools minimise dead freight risk as the booked freight capacity is matched with the actual associated operations, providing efficiency to charterer operations and enhancing the global shipping supply chain.
Handy Bulk
Handy Bulk provides dry bulk market intelligence, freight prediction, and operational apps to assist charterer teams in preventing the occurrence of dead freight. Its cargo intelligence facilitates correct planning of cargo, usage of space, and planning, leading to better decision-making between owners and operators in maritime freight contracts.
Freight Course
Freight Course offers freight operation training on what dead freight is in shipping, how to calculate it, and how to optimise contracts. Its resources assist charterers and shipping professionals to avoid overbooking, be better able to handle cargo, and avoid nasty surprise dead freight claims in international commerce.
How Does Dead Freight Influence Logistics and Customs Processing?
Dead freight may slow shipping schedules, complicate customs documentation and cause cargo inefficiencies. Effective planning will reduce these risks to ensure compliance and on-time delivery within international trade corridors.
How to Minimise Dead Freight?

Embrace Flexible Booking Terms
A more flexible, available freight booking policy will minimise the impact of volume fluctuations, avoiding contractual breaks and reducing dead freight liabilities. This elasticity also builds long-term carrier relationships so that they are prioritised in the peak shipping seasons.
Maximise Loading Efficiency
Optimisation of loading by dry bulk and container shipments increases the utilisation of available spaces to prevent wastage, which lowers shipping costs. Use of well-trained loading crews and optimal stowage plans further optimises the use of space.
Formalise Clear, Dead Freight–Safe Contracts
Understandable contracts specify the expectations of both parties, charterer and vessel owner, lessening the probability of mismatches. Detailed conditions safeguard both parties and also guarantee proper usage of freight space. It can help to prevent unnecessary dead freight situations by including penalty clauses against underutilisation as well.
Hone Forecasting and Cargo Planning
The use of advanced cargo forecasting allows accurate bookings to be made in shipping, as overestimating may result in dead freight penalties. Forecasting accuracies are further enhanced by periodically checking the market demand data.
Track Your Shipments in Real Time
The real-time tracking systems ensure up-to-date information about the state of the cargo by allowing alteration of plans within comparatively short periods in order to avoid the problem of dead freight in dynamic freight markets. The easier response to last-minute changes is made possible through integration with inventory systems.
Work Closely with Your Logistics Network
Good cooperation with your logistics partners, brokers, and charterers will result in a more effective matching of the freight capacity to the practical shipping requirements, reducing the risk of dead freight. Constant contact creates confidence and resolves unexpected issues easily.
FAQs
1) What exactly is dead freight?
Dead freight refers to the amount paid by a charterer to occupy cargo space they do not ship, guaranteeing that a ship owner will be paid to ship in shipping agreements.
2) How do you figure out the cost of dead freight?
This amount is computed based on the contracted goods and the actual number of goods loaded, times the agreed rate of freight, in accordance with provisions of either the charterer agreement or the shipping contract.
3) What strategies can help avoid dead freight charges?
The risk of dead freight can be avoided through proper cargo forecasting, contractual flexibility, efficient loading, draughted shipping contracts and effective communication among the shippers, brokers and the charterer.
4) How is dead freight defined in shipping agreements?
Dead freight, in a shipping contract, is stipulated as a payment to be made due to the charterer reserving space with less cargo being loaded on board than agreed under a charter party.